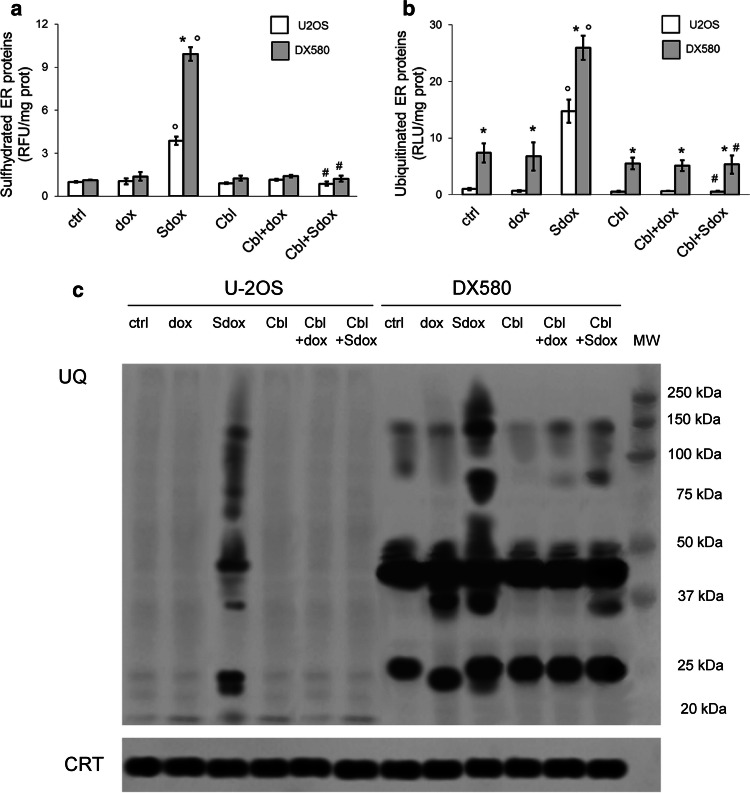
Fig. 4.
H2S-releasing doxorubicin increases sulfhydration and ubiquitination of ER-associated proteins. U-2OS and U-2OS/DX580 cells were grown in drug-free medium (ctrl) or in the presence of 5 µM doxorubicin (dox) or H2S-releasing doxorubicin (Sdox) for 24 h. When indicated, the H2S-scavenger hydroxy-cobalamin (100 µM, Cbl) was co-incubated. Cells were lysed and microsomal fractions were isolated. a Fluorimetric analysis of sulfhydrated microsomal proteins, performed in triplicates. Data are mean ± SD (n = 5 independent experiments). *p < 0.001 for U-2OS/DX580 cells vs. U-2OS cells; °p < 0.001 for Sdox-treated cells vs untreated (ctrl) or dox-treated cells; #p < 0.001 for Cbl-treated cells vs. corresponding cells without Cbl. b Ubiquitination of microsomal proteins, measured by a chemiluminescence-based assay in triplicates. Data are mean ± SD (n = 5 independent experiments). *p < 0.001 for U-2OS/DX580 cells vs. U-2OS cells; °p < 0.001 for Sdox-treated cells vs untreated (ctrl) or dox-treated cells; #p < 0.001 for Cbl-treated cells vs. corresponding cells without Cbl. d. Microsomal proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and probed with an anti-mono/poly-ubiquitin (UQ) antibody. The caltreticulin (CRT) expression was used as control of equal protein loading. MW molecular weight. The figure is representative of one out of four experiments