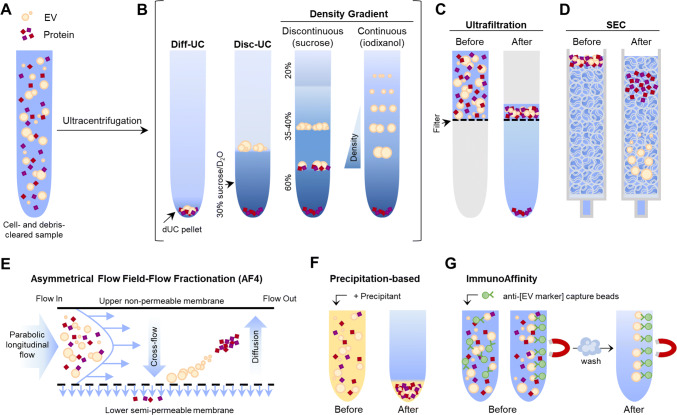
Fig. 2.
Graphical summary of mainly used EV isolation methods. a The starting sample is a cell- and debris-cleared biofluid containing EVs and proteins in suspension. b Ultracentrifugation renders an EV pellet that also contains proteins (dUC pellet), which can be further purified by discontinuous ultracentrifugation (disc-UC), like floatation in a sucrose cushion, or by density gradient (DG) ultracentrifugation: in a discontinuous gradient using different sucrose solutions or in a continuous, self-making gradient using solutions of iodixanol (optiprep). This way, proteins and the different EV populations are separated by their density. Ultrafiltration (c), size-exclusion chromatography (SEC; d) and asymmetrical flow filed-flow fractionation (AF4; e) separate molecules by their hydrodynamic radius (size). c Ultrafiltration is a dead-end filtration system that allows the separation of molecules according to the molecular weight cutoff (size) of the filter pore used. It renders a mixed sample of EVs and proteins, but allows great sample volume reduction. d In SEC, the first to elute are the molecules bigger than the matrix pores (EVs), while smaller particles within the fractionation range (proteins) get slowed down by entering the matrix bead pores and so elute later on. e In AF4, a cross-flow (field) perpendicular to the longitudinal laminar flow forces particles towards the semipermeable membrane. Particles smaller than the membrane pore are removed through the membrane. Retained ones migrate away due to diffusion and flow in the equilibrium position of the two forces (field and diffusion) according to their size. The velocity of the longitudinal flow increases parabolically, thus smaller particles, in the centre of the flow, are carried faster and elute before bigger ones. This way, proteins and differently sized EV populations are separated. f Precipitation-based isolation relies on the addition of water-excluding precipitants like PEG to concentrate all particles in one pellet. g Immunoaffinity isolation is based on EV capture using a specific antibody that recognizes an EV-specific marker, coupled to beads that can be separated by centrifugation or magnetically (like depicted). Given the lack of pan-EV markers, not all EV populations are isolated. Original graphical artwork