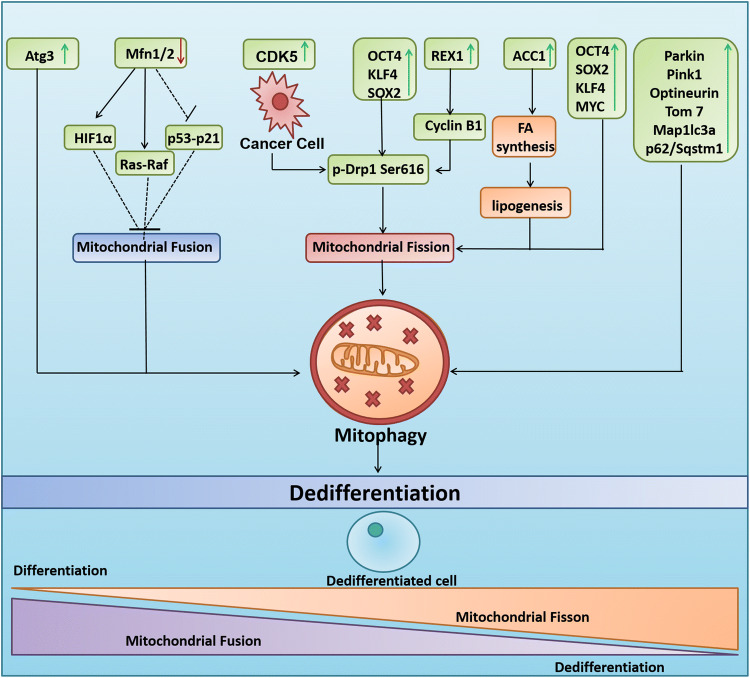
Fig. 3.
Mitophagy regulates cellular pluripotency. Induction of mitophagy via the activation of mitochondrial fission through the OCT4, KLF4 and SOX2 cocktail, cyclin b1 dependent DRP1 Ser (S) 616 phosphorylation, ACC1 enzyme mediated lipogenesis leads to the dedifferentiation of somatic cells into stem cells. Moreover, the inhibition of mitochondrial fusion by reduced expression of MFN1 leads to activation of HIF1α and Ras–Raf and inhibition of p53–p21 which further leads to mitophagy-mediated acquisition of pluripotency. REX1, ACC1, Parkin, PINK1, Optineurin, TOM7, MAP1LC3a, p62/Sqstm1 and ATG3 are also implicated in inducing pluripotency through the activation of mitophagy. The activation of CDK5 in cancer cells leads to the phosphorylation of DRP1 at Ser (S) 616 leading to mitochondrial fission, mitophagy and cancer stemness