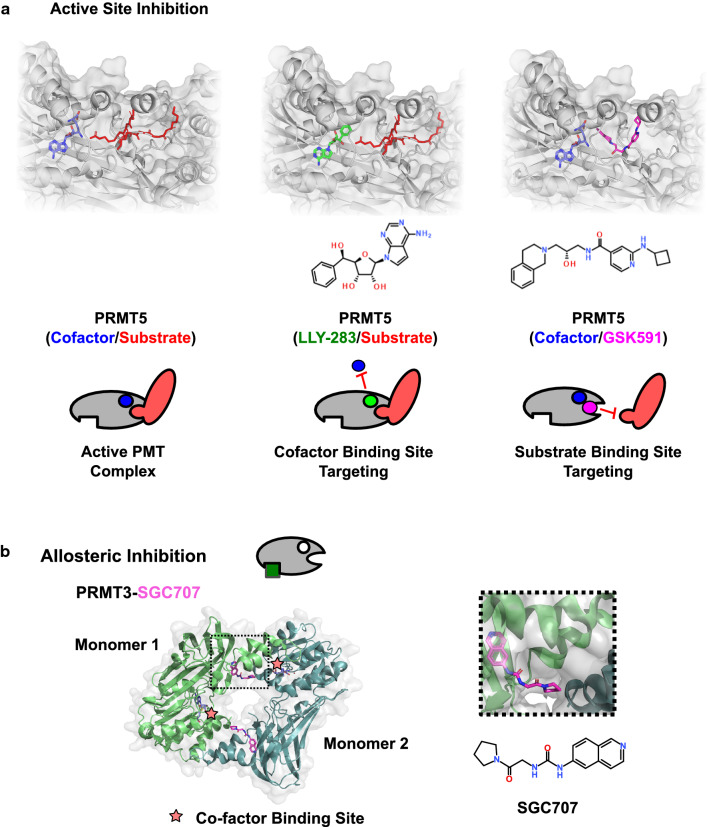
Fig. 3.
Mechanisms of enzymatic PMT inhibition. a Substrate peptide and SAM cofactor bind at distinct sites in the active site, as shown in a crystal structure of PRMT5 with H4 peptide substrate and SAM analogue cofactor (PDB: 4GQB). Active site inhibition can be achieved by targeting either cofactor or substrate-binding site. Examples shown include LLY-283 cofactor site binding (PDB: 6CKC) and GSK591/EPZ015866 binding to the substrate peptide channel (PDB: 5C9Z). b Structure of the allosteric inhibitor SGC707 bound to a biological assembly of PRMT3 (PDB: 4RYL). SGC707 binds at the interface between dimers to block formation of the active homodimer