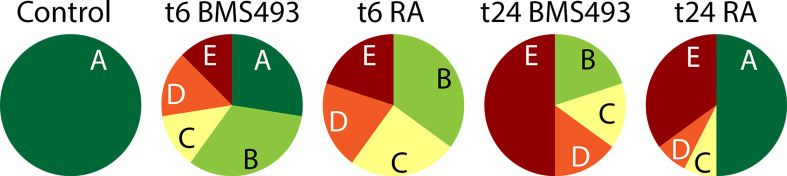
Fig. 1.
Effects of retinoic acid (RA) signaling alterations on mechanoreception in amphioxus larvae. Amphioxus embryos were exposed to DMSO (control), the RA receptor (RAR) antagonist BMS493 or all-trans RA, starting from the treatment time points (t): 6 or 24 hpf (hours post fertilization). For each treatment condition, the responses of n = 50 larvae at the 48 hpf stage to a mechanical stimulus were assessed and counted. The response A (dark green) corresponds to a quick muscular swimming movement away from the stimulus and was shown by all control animals, the response B (light green) to an intense wiggling and bending movement without clear directionality, the response C (yellow) to a short wiggling motion on the spot, the response D (orange) to short disconnected twitches or bends on the spot, and the response E (red) to no visible movement or reaction