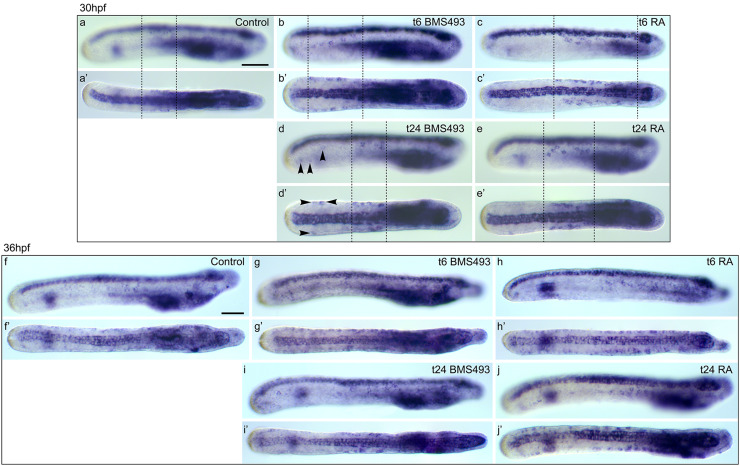
Fig. 11.
Effects of retinoic acid (RA) signaling alterations on the development of soxb1c-expressing cells in amphioxus. a–e′ Larvae at 30 hpf (hours post fertilization) and f–j′ larvae at 36 hpf are shown in lateral view (a–j) and dorsal view (a′–j′). All images are focused only on soxb1c-expressing cells in the ectoderm. a, a′, f, f′ Control animals treated at 6 hpf with DMSO. b, b′, d, d′, g, g′, i, i′ Animals treated with the RA receptor (RAR) antagonist BMS493 at two different developmental stages, 6 or 24 hpf. c, c′, e, e′, h, h′, j, j′ Animals treated with all-trans RA at two different developmental stages, 6 or 24 hpf. The treatment time point (t), 6 or 24 hpf, is indicated in the right upper corner of each image set. a–e′ Dotted lines mark the ectodermal domain that contains soxb1c-expressing ectodermal sensory neuron progenitors (ESNPs) (compare with Additional file 9: Figure S6). d, d′ Arrowheads mark soxb1c-expressing ESNPs that are induced specifically in the tail ectoderm of early larvae, which had been treated with BMS493 at 24 hpf. Scale bars are 50 µm. The scale bar in a also applies to a′, b–e′, and the scale bar in f also applies to f′, g–j′