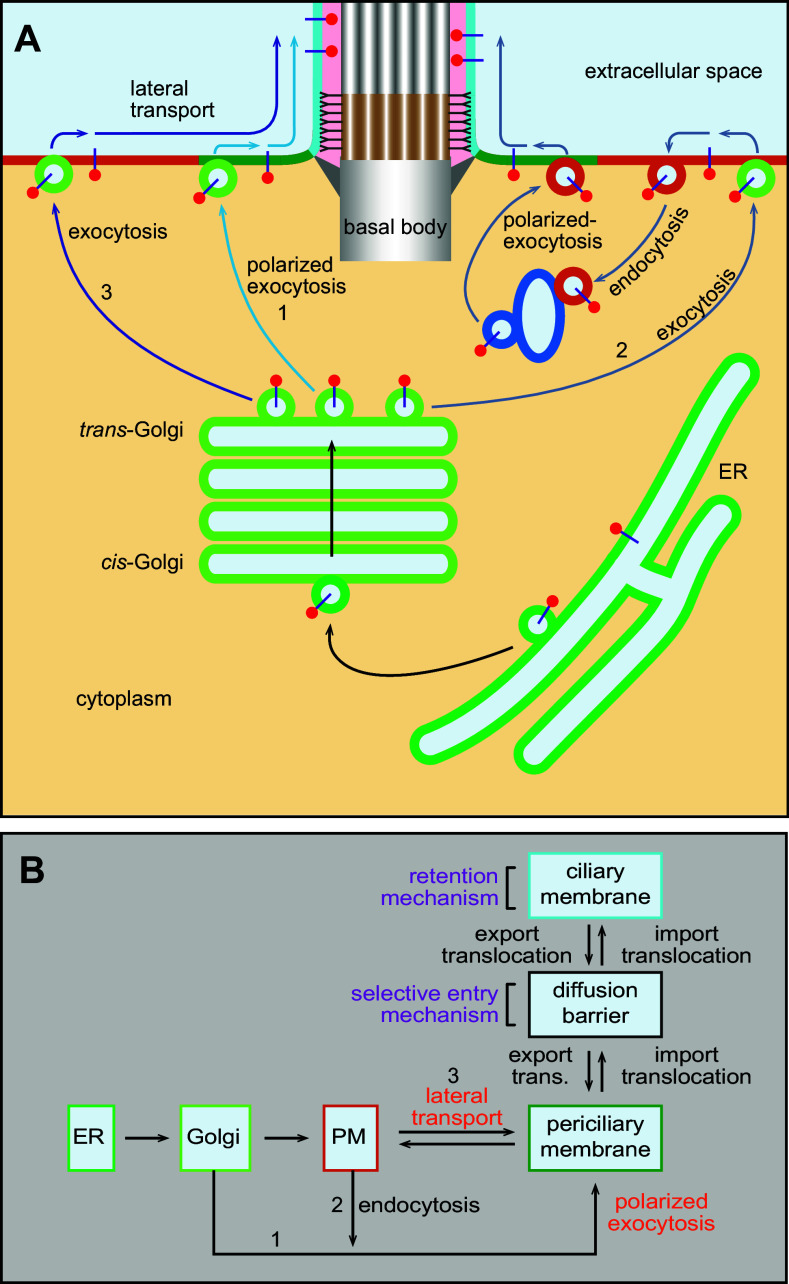
Fig. 2.
Targeting ciliary membrane cargoes to the periciliary membrane by the lateral transport or polarized exocytosis. a Ciliary membrane cargoes are synthesized in the ER and subsequently enter the secretory pathway to the Golgi apparatus. At the TGN, cargoes can take different pathways to the periciliary membrane. In pathway 1, packed into vesicles from the TGN, cargoes can target to the periciliary membrane directly via polarized exocytosis or indirectly, as illustrated by pathway 2, by first to the PM, followed by endocytosis to the endosome and at last to the periciliary membrane by polarized exocytosis. Alternatively, in pathway 3, cargoes are delivered to the PM by constitutive exocytosis from the TGN and they subsequently enter the periciliary membrane by lateral transport. b Flow chart showing the ciliary trafficking pathways and models among various organelles and membrane domains, including the ER, Golgi, PM, periciliary membrane, membrane diffusion barrier, and ciliary membrane. Note that steps marked by two opposite arrows are reversible. 1, 2, and 3 correspond to pathways 1, 2, and 3, respectively, as described in a. export trans. export translocation