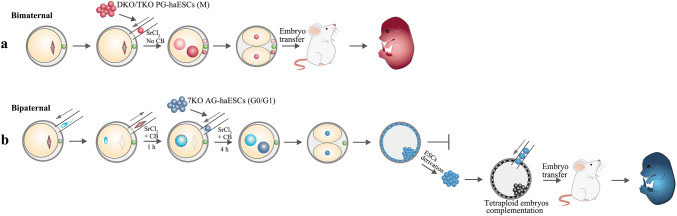
Fig. 4.
Schematics showing the procedures used to generate unisexual animals. a Bimaternal mice are produced through the injection of M-phase DKO PG-haESCs into intact MII oocytes. b Bipaternal embryos are generated by injecting G0/G1 phase 7KO AG-haES cells into androgenetic haploid embryos that were previously injected with a sperm head, followed by the removal of the maternal spindle. The developmental potential of these bipaternal embryos is limited to E8.5 after embryo transfer. However, bipaternal mice are able to be obtained by an alternative strategy through a tetraploid embryo complementation assay after the derivation of bipaternal diploid ESCs