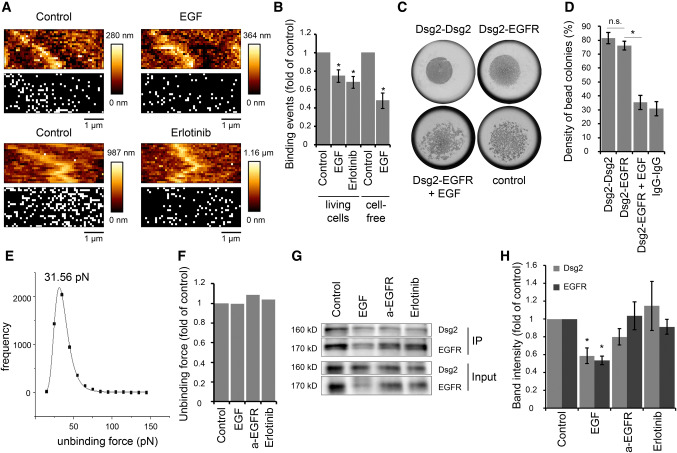
Fig. 3.
EGF reduces Dsg2-specific binding events on the cell surface of living DLD1 cells. a Dsg2 adhesion measurements were performed on living DLD1 cells under control conditions and after incubation with EGF or erlotinib. Shown are topography images of selected areas at cell borders and adhesion maps with each white pixel representing one binding event. b Quantification shows a significant reduction of binding events on living DLD1 cells after incubation with both, EGF or erlotinib. Application of EGF also reduced the amount of binding events in the cell-free AFM setup with a Dsg2-coated tip and EGFR-coated mica sheets. Graph bars represent fold-change values ± SE from at least four independent experiments. *p < 0.05. c Peak fit analysis of measured unbinding forces revealed a distribution peak of 31.56 pN under control conditions. d Distribution-peak values of unbinding forces measured on DLD1 cells under control conditions and after incubation with EGF, anti-EGFR antibody, or erlotinib were compared and revealed similar values for all conditions. Graph shows distribution-peak values normalized to control. e, f Hanging drop bead aggregation assay confirms blockade of interaction between Dsg2 and EGFR through EGF. Beads coated with a human IgG Fc fragment served as control. *p < 0.05; n.s. not significant. g Western blot analysis of surface biotinylation assay revealed reduced Dsg2 and EGFR levels on the surface of DLD1 cells after incubation with EGF. h Quantification of Dsg2 and EGFR band intensity from at least seven independent experiments shows a significant reduction of surface protein levels only after incubation with EGF. Graph bars represent fold-change values ± SE. *p < 0.05