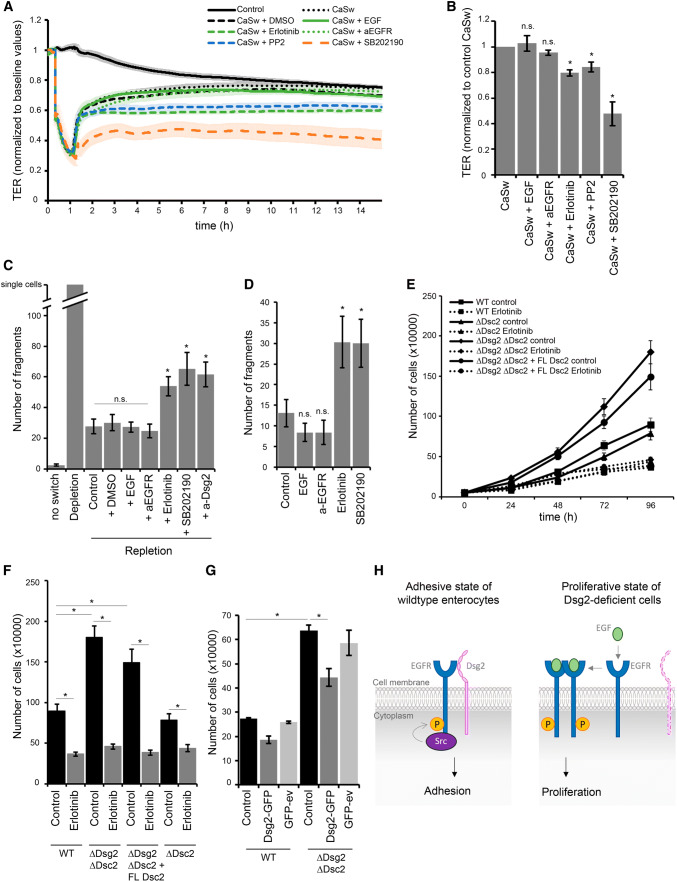
Fig. 5.
Dsg2 regulates EGFR activity, thereby suppressing proliferation and supporting an adhesive state in enterocytes. a Barrier recovery of DLD1 WT cells after Ca2+ switch was monitored via TER measurements showing impaired barrier recovery after inhibition of EGFR, Src and p38MAPK activity with respective inhibitors. Inhibitors were applied together with CaCl2 after 1 h depletion with EGTA. b TER values were quantified after 10 h of repletion with respective inhibitors and normalized to control repletion with respective vehicle. Repletion with erlotinib, PP2, and SB202190 resulted in significantly reduced TER values compared to control. Shown are fold-change values ± SE of 4–6 independent experiments. *p < 0.05; n.s. not significant. c Cell adhesion of DLD1 cells was analyzed in a dispase-based dissociation assay after Ca2+ switch and treatment with several inhibitors. Treatment with erlotinib, PP2, and SB202190 during repletion significantly increased monolayer fragmentation compared to control repletion with respective vehicle. Shown is mean ± SE of six independent experiments. *p < 0.05; n.s. not significant. d Confluent DLD1 cell monolayer were treated with EGF, a-EGFR, erlotinib, or SB202190, and analyzed for cell adhesion in a dispase-based cell dissociation assay. Inhibition of EGFR and p38MAPK activity significantly increased number of fragments in contrast to EGF and the EGFR-specific antibody. Shown is mean ± SE of five independent experiments. *p < 0.05; n.s. not significant. e Cell proliferation was determined by cell counting. 50,000 cells were seeded for each cell line with or without erlotinib and cells were counted after 24, 48, 72, and 96 h. f Number of cells after 96 h was quantified. Shown is mean ± SE of at least five independent experiments. *p < 0.05. g Cell proliferation was determined after Dsg2 reconstitution in DLD1 cells deficient for Dsg2 and Dsc2, 48 h after transfection. Shown is mean ± SE of four independent experiments. GFP-ev empty vector, *p < 0.05. h Model of Dsg2-mediated regulation of EGFR. Dsg2 recruits EGFR to cell borders where it is phosphorylated by Src and induces downstream signaling, thereby strengthening adhesion maybe via p38MAPK. Loss of Dsg2 results in activation of the canonical EGFR signaling pathway resulting in proliferation