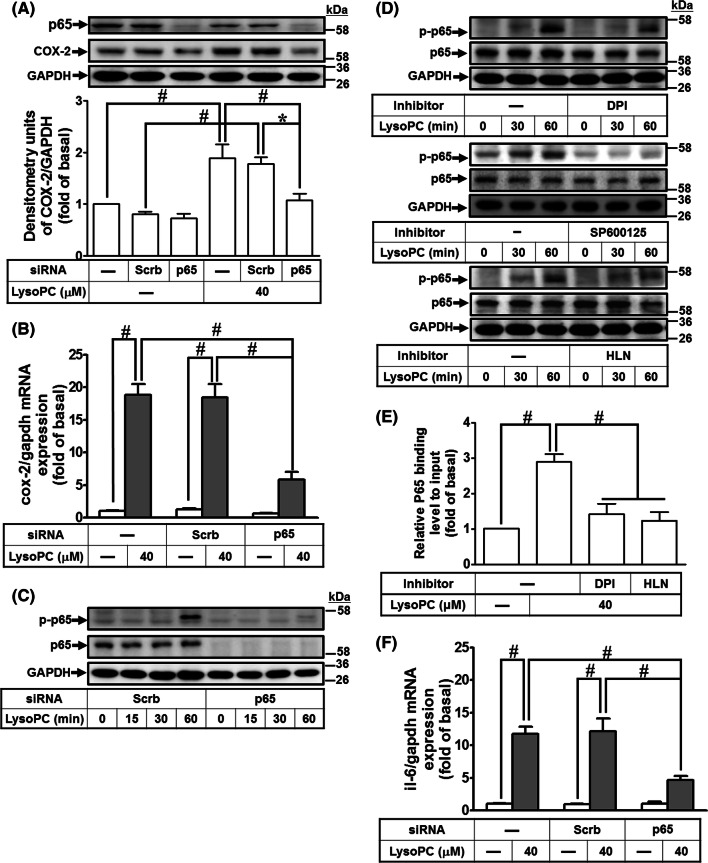
Fig. 3.
NF-κB is involved in LysoPC-induced COX-2 and IL-6 expression. a, b HCFs were transfected with siRNA of scramble or p65 and then treated with LysoPC for 6 h. a The levels of p65, COX-2, and GAPDH protein were determined by western blot (n = 6). b The levels of COX-2 and GAPDH mRNA were determined by RT/qPCR (n = 6). c HCFs were transfected with siRNA of scramble or p65, and then treated with LysoPC for the indicated time intervals. The levels of p65, phospho-p65, and GAPDH protein were determined by western blot (n = 6). The densitometry measurements of phospho-p65 are presented in Supplementary Fig. 3A. d HCFs were pretreated with DPI (100 nM; n = 7), SP600125 (1 μM; n = 5), or helenalin (HLN, 1 μM; n = 7) for 1 h, and then treated with LysoPC for the indicated time interval. The levels of p65, phospho-p65, and GAPDH protein were determined by western blot. The densitometry measurements of phospho-p65 are presented in Supplementary Fig. 3B–D. e HCFs were pretreated with DPI (100 nM) or helenalin (1 μM) for 1 h, and then incubated with LysoPC for 1 h. The DNA binding activity of NF-κB was determined by a ChIP assay. Quantification of p65 immunoprecipitated DNA was performed by an SYBR system for qPCR, and the results are shown as the fold change normalized to input control (n = 4). f HCFs were transfected with siRNA of scramble or p65, and then treated with LysoPC for 6 h. The levels of IL-6 and GAPDH mRNA were determined by RT/qPCR (n = 6). Data are presented as mean ± SEM, and analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc tests. *p < 0.05; #p < 0.01