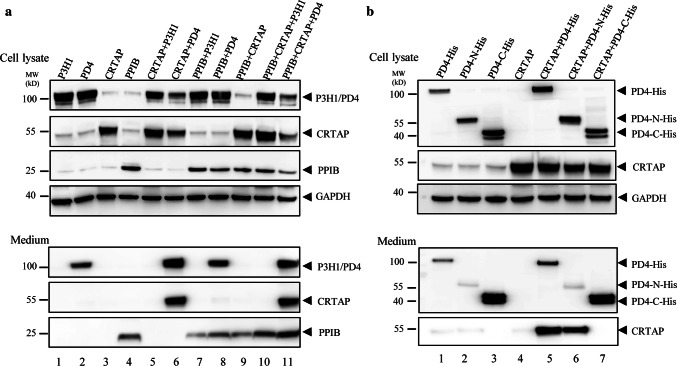
Fig. 2.
The role of KDEL in co-translocation of P3H1/CRTAP. a Transfection of various combinations among P3H1, PD4, CRTAP, and PPIB into cells, followed by the analysis of the media and cell lysates by western blot. Wild-type P3H1 and CRTAP were almost all retained in the cells in HEK 293E cell lines (lanes 1, 3, 5, and 10). Substantial amount of the PD4 was secreted into the medium (lane 2), while large amount of CRTAP was secreted along with PD4 (lanes 6 and 11). This shows the importance of the KDEL sequence in the retention of both P3H1 and CRTAP in ER. GAPDH in the cells was blotted as a loading control. b The full-length of PD4-His, the N-terminal segment of PD4 (PD4-N-His), and the C-terminal dioxygenase domain of PD4 (PD4-C-His) were transfected alone or with CRTAP. The samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blot. Both domains of P3H1 could be secreted into the culture medium, and CRTAP was mostly retained in the cells; however, when co-expressed with PD4-His (lane 5) or PD4-N-His (lane 6), substantial amount of CRTAP was secreted into the medium. Little CRTAP was detected in the medium when it was co-expressed with PD4-C-His (lane 7). All experiments were performed ≥ 3 times independently