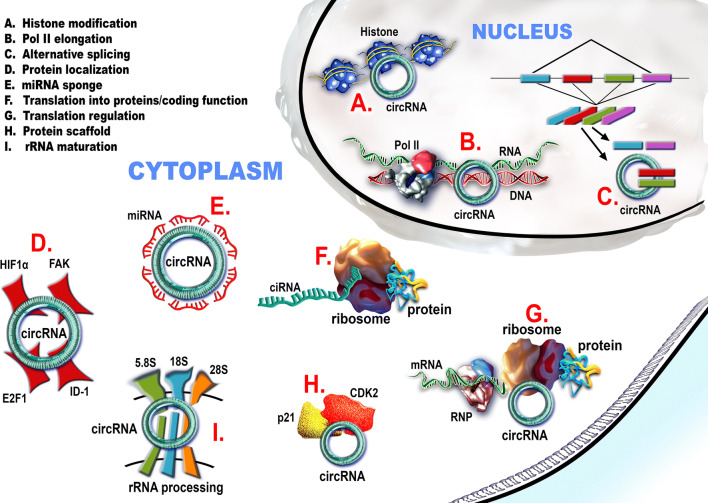
Fig. 2.
Circular RNAs (noted circRNA—for all circular RNA types) fulfill multiple functions inside the cell. In the nucleus a–c circRNAs can a interact with the histone methylation pattern and silence a specific locus; b regulate the transcription of their gene of origin through direct (circRNAs) or snU1-mediated (EIcircRNA) interaction with the RNA polymerase II; c compete with the mRNA for the available splicing machinery and interfere in the alternative splicing process. In the cytoplasm d–i the circRNAs can: d entrap certain transcription factors in the cytoplasm; e act as miRNAs sponges, especially the circRNAs with exon-containing transcripts; f be translated into proteins. g circRNAs interact with RNA-binding proteins and regulate the translation of some mRNAs. h circRNAs can act as protein scaffolds. They can entrap some proteins and impair their signal transduction role. i circRNAs can induce apoptosis by interfering within the processing of pre-rRNA subunits