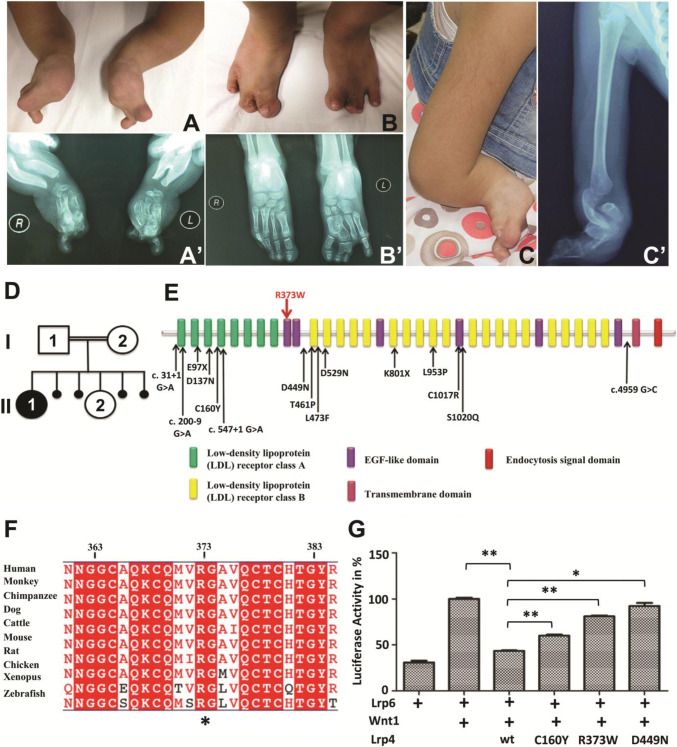
Fig. 6.
Phenotypic characteristics of investigated patient with typical Cenani-Lenz syndactyly syndrome caused by a point mutation in LRP4. The picture (a) and X-ray radiograph (a′) of patient’s hands, the picture (b) and X-ray radiograph (b′) of patient’s feet, showing syndactyly, disorganized metacarpal and phalangeal bones. The picture (c) and X-ray radiograph (c′) of patient’s right upper limb, showing short forearms and radius-ulnar synostosis. d The patient, female (II:1), was born to first cousin parents (I:1 and I:2) with one unaffected child (II:2) and four abortions. e Schematic view of LRP4 domains and localization of identified CLS mutations, where the novel mutation R373W is labeled by the red arrow and other known mutations labeled by black arrows. f LRP4 is highly conserved across different vertebrate species; the conserved R373 is highlighted with a star (*). g The effect of R373W mutation and LRP4 knockdown on the Wnt signaling in vitro. TOP-Flash luciferase assay was performed to quantify the Wnt activity in HEK293T cells co-transfected with Lrp6, Wnt1, and the indicated Lrp4 cDNA. Values represent mean ± SE of data from three independent experiments, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (Student’s t test)