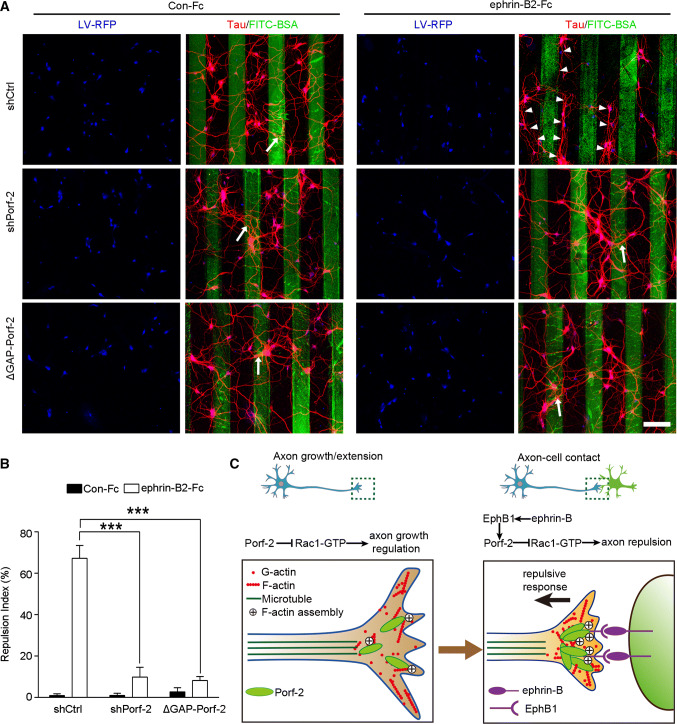
Fig. 9.
Porf-2 is required for EphB1 mediated axon repulsion. a Representative images of axon morphology in shCtrl-, shPorf-2- or ΔGAP-Porf-2-transfected neurons on ephrin-B2-Fc- or Con-Fc-containing stripes. Scale bar: 100 μm. The cells were transfected with indicated virus (blue) and stained with tau (red). Arrows indicate axons crossing the stripe and arrowheads indicate axon bundles that grow in the space between the stripes. b The quantification of the axonal repulsion index. Repulsion index (%) = non-crossed axon number/total axon number × 100. All experiments were performed ≥ 3 times independently. Error bars represent ± SEM; ***P < 0.001. c Schematic drawing demonstrating a previously uncharacterized mechanism for Porf-2 through inactivation of Rac1/F-actin via its GAP domain either in inhibiting filopodia formation and neurite branching during initial axon growth/extension (left panel), or in transduing EphB-mediated forward signaling upon axon–cell contact, which brakes axon growth and leads to growth cone repuslion (right panel)