Fig. 1.
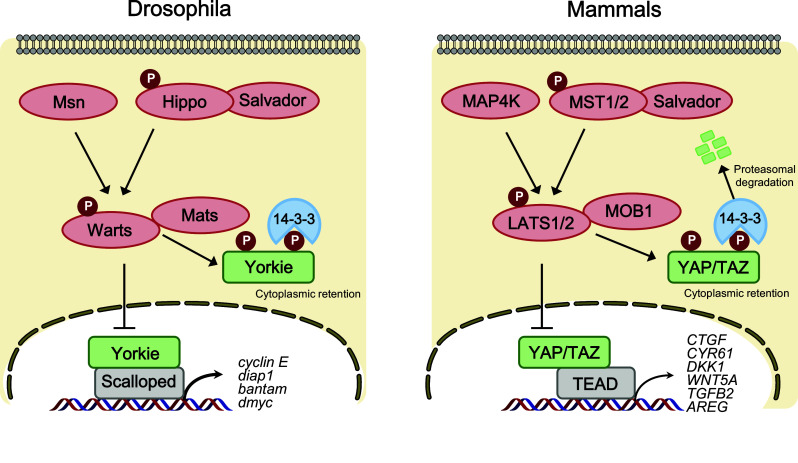
Core Hippo pathway components in Drosophila and mammals. In Drosophila (left), Hippo (Hpo) and Misshapen (Msn) kinase phosphorylate and activate Warts (Wts) kinase, which in turn inactivate the transcriptional co-activator Yorkie (Yki). Phosphorylation of Yki leads to cytoplasmic retention via a 14-3-3 interaction. Upon Hippo pathway inactivation, dephosphorylated Yki translocates to the nucleus and binds the transcription factor Scalloped (Sd) to induce gene expression involved in cell proliferation and anti-apoptosis. In mammals (right), the core Hippo pathway components are evolutionarily conserved. MST1/2 kinase phosphorylates LATS1/2, which in turn phosphorylates and inhibits YAP/TAZ. Phosphorylation of YAP/TAZ leads to cytoplasmic sequestration and proteasomal degradation
