Fig. 2.
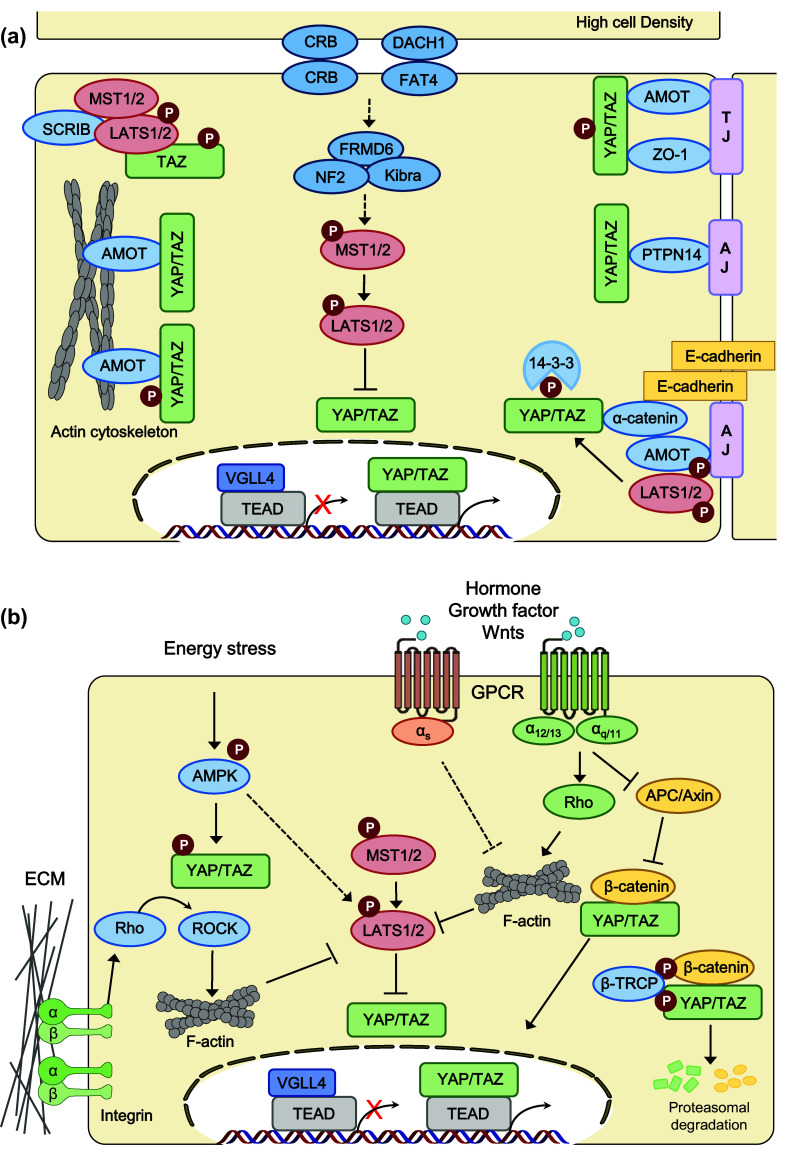
Regulators and regulations of the Hippo pathway. Hippo pathway components in mammals are shown in various colors. Pointed arrows indicate activation, and blunt-ended lines indicate inhibition. Hippo cascade kinases are shown in red and inhibitory regulators of YAP/TAZ activity are shown in blue. a Hippo pathway is regulated by cell polarity (Crumbs, DACH1–FAT4) and cell–cell junctions (adherens junction, tight junction). AMOT angiomotin, AJ adherens junction, CRB Crumbs homolog, DACH1 Dachous-1, FRMD6 FERM domain-containing protein 6, LATS large tumor suppressor homolog, MST mammalian STE20-like protein kinase, NF2 neurofibromin 2 (also known as Merlin), PTPN14 protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 14, SCRIB scribbled planar-cell polarity protein, TAZ transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif, TJ tight junction, VGLL4 vestigial-like protein 4, YAP Yes-associated protein, ZO zona occludens protein. b Hippo pathway is regulated by extracellular ligands, stress responses, and mechanotransduction. AMPK 5′ AMP-activated protein kinase, APC adenomatous polyposis coli, β-TRCP β-transducin repeat-containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase, ECM extracellular matrix, GPCR G protein-coupled receptor, Rho Ras homolog gene family, ROCK Rho-associated protein kinase
