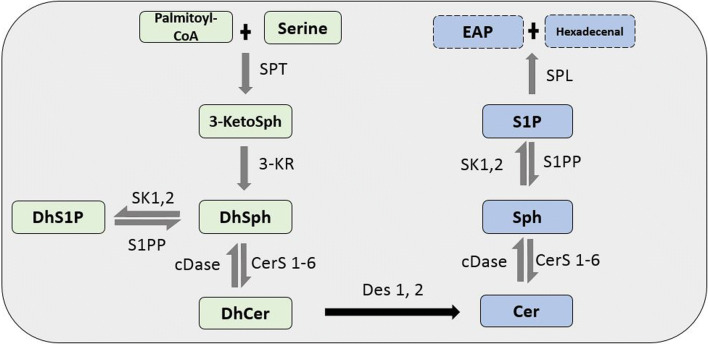
Fig. 1.
De novo sphingolipid biosynthesis pathway. In the de novo pathway, the condensation of palmitoyl-CoA and serine by the enzyme SPT forms 3-ketoSph. This is then reduced by 3-KR to dhSph. The acylation and phosphorylation of dhSph by CerS1-6 and SK 1 and 2 leads to the formation of dhCer and dhS1P, respectively. Des-1 and -2 then catalyze the desaturation of dhCer to Cer, which is a non-reversible reaction. The metabolization of Cer by CDase produces Sph. The production of S1P from Sph is exclusively phosphorylated by SK 1 and 2. S1P is then degraded to ethanolamine phosphate (EAP) and trans-2-hexadecenal by S1P lyase (SPL). DhS1P and S1P can be converted back to dhSph and Sph by S1P phosphatase (S1PP) and dhSph and Sph to dhCer and Cer, respectively, by cDase