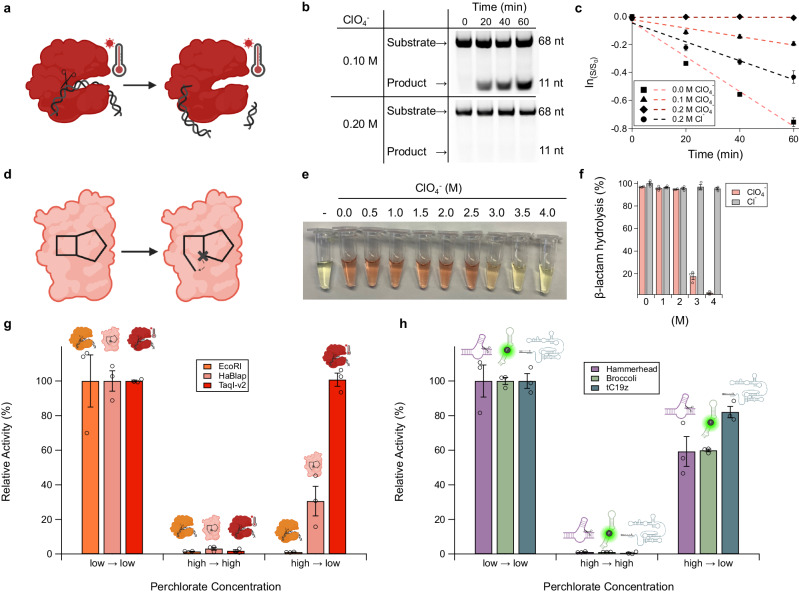
Fig. 2. Recovery of activity by functional RNAs from perchlorate-induced denaturation is general, while it is limited to only extremophilic protein enzymes.
a Cartoon depiction of TaqI-v2 nuclease cleaving dsDNA. b Gel images of TaqI-v2 nuclease assay (0.05 U/µL EcoRI, and 1 µM duplex DNA) in perchlorate solutions showing the enzyme is inactive at 0.2 M perchlorate. c Rate measurements of TaqI-v2 nuclease assay with NaCl control. d HaBlap hydrolase opens a β-lactam ring. e HaBlap activity assay (5 µM of HaBlap and 50 µM nitrocefin in 5 mM phosphate buffer pH 7) in perchlorate brines performed with the colorimetric β-lactamase substrate nitrocefin. f Yields of HaBlap reactions compared to NaCl controls. g Activity recovery assay performed on the proteins EcoRI, HaBlap, and TaqI-v2, showing recovery occurs upon dilution from high to low salt only in extremophilic proteins. High and low perchlorate solutions were 5 and 0.05 M, respectively. h Activity recovery assay performed on the functional RNAs hammerhead ribozyme, Broccoli aptamer, and tC19z ribozyme, showing recovery occurs upon dilution from high to low salt in all three RNAs. High and low perchlorate solutions were 8 and 0.8 M for hammerhead and Broccoli and 5 and 0.5 M for tC19z. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean with n = 3 independent experiments. Figure 2a, d, g, and h created with BioRender.com released under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 International license.