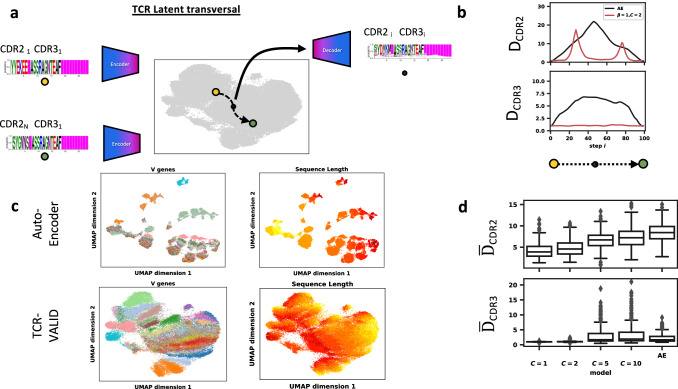
Fig. 2. TCR-VALID learns a smooth and realistic embedding of TCRs.
a Illustration of TCR latent transversals to evaluate embedding landscape smoothness: two TCR sequences (CDR2-3) with identical CDR3 but differing CDR2 are embedded into the learned latent space. A linear interpolation between TCRs in latent space is then decoded back into sequence space and evaluated. b The distance between TCR-VALID (red) and auto-encoder (black) decoded interpolated TCRs and training TCR sequences for CDR2 (Dcdr2 metric, top) and CDR3 (Dcdr3, bottom) n = 100 interpolated points per trajectory, c UMAP embedding for subset of TCR training sequences for auto-encoder (top) and TCR-VALID (bottom) colored by V gene usage (left panel) and sequence length (right panel). d Averaged distance over the whole trajectory for many Monte Carlo selected latent space transversals for both CDR2 ( metric, top) and CDR3 ( metric, top). Box plots are shown with lines for quartiles, whiskers extend to 1.5 times the interquartile range, and outliers above or below the whiskers are displayed as points. n = 310 traversals per boxplot. Source data for b–d are provided as a Source Data file.