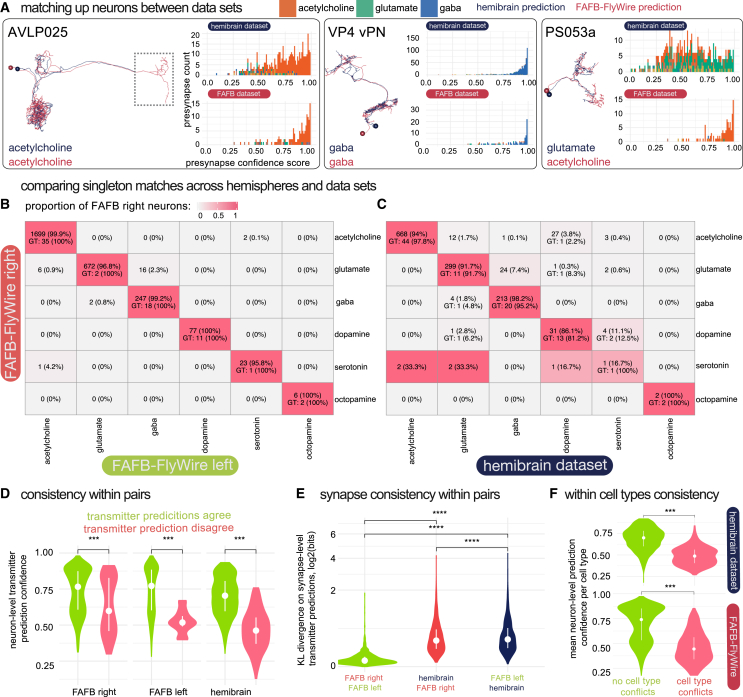
Figure 4.
Comparing neuron-level transmitter predictions between connectome datasets from separate animals and between hemispheres
(A) Images of co-registered, matched neurons between the HemiBrain (navy) and the FAFB-FlyWire (red) datasets. Histograms show synapse-level transmitter prediction scores for exemplar pairs. Neurons can be matched despite missing data (left, grey dashed box). PS053a has conflicting neuron-level transmitter predictions.
(B) Confusion matrix compares matched singleton FAFB-FlyWire-right and FAFB-FlyWire-left pairs’ neuron-level transmitter predictions (1,586 pairs).
(C) Confusion matrix comparing matched FAFB-FlyWire-right and HemiBrain-right neuron-level transmitter predictions (1,318 pairs). Cells colored by the proportion of FAFB-FlyWire right neurons of each transmitter type (row normalized) that are matched to its homolog-columns give homolog prediction.
(D) Neuron-level transmitter prediction scores between matched singletons that have (red, right) or do not have (green, left) a conflict between their neuron-level transmitter predictions, across all three hemispheres. Matches:mismatches across all comparisons for FAFB-FlyWire right: 2,650:170 FAFB-FlyWire left, 1,562:40, and HemiBrain neurons, 1,088:130.
(E) Comparison of similarity scores for matches (Kullback-Leibler divergence on synapse-level transmitter prediction scores).
(F) The neuron-level transmitter prediction consistency among cell types that have multiple repeats, i.e., not singletons. Green, the mean neuron-level transmitter prediction confidence for cell types where all members of the type are predicted to use the same transmitter. Red, the mean neuron-level transmitter prediction confidence for cell types where not all members of the type are predicted to use the same transmitter. Violin plots show the median value (dot) and the inter-quartile range (line, 25th to 75th percentiles). Data were compared using Wilcoxon two-sample tests (n.s., not significant; ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001; ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.00001.