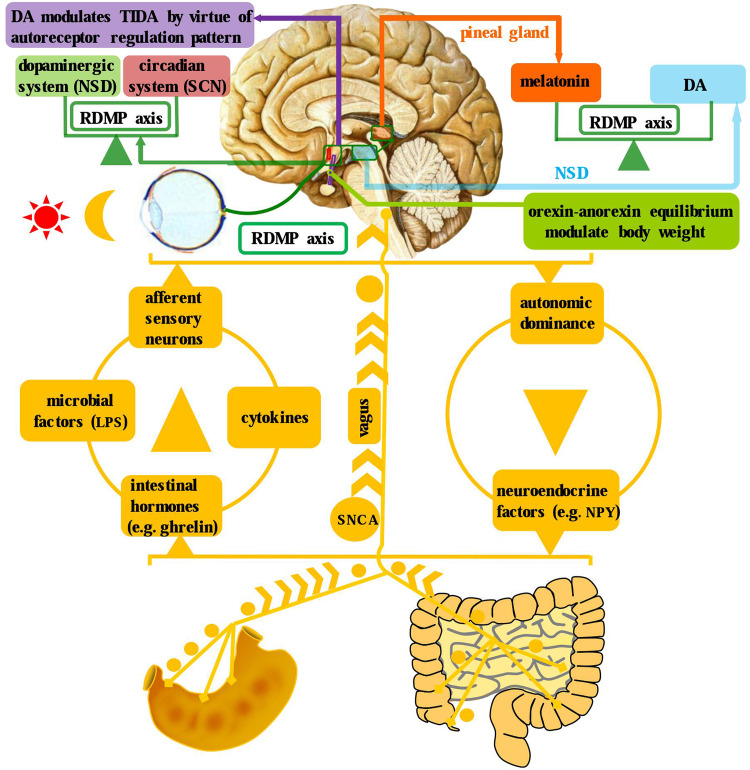
Fig. 4.
Brain–gut axis, dopaminergic system, and circadian system in the neuroendocrine context of PD. There exist bidirectional communications between brain and gut, which enable these two entities to be an integrated complex. In particular, there are four ascending pathways from the gut to brain: afferent sensory neurons, microbial factors, intestinal hormones, and cytokines. While there are two avenues from the brain to gut: autonomic dominance and neuroendocrine factors. Besides, a cross talk is identified between the circadian (SCN) and dopaminergic (NSD) systems, specifically manifesting as the DA and melatonin yoking in the RDMP axis. Moreover, the infundibular orexin–anorexin equilibrium and dopaminergic auto-receptor regulation of TIDA is illustrated as well