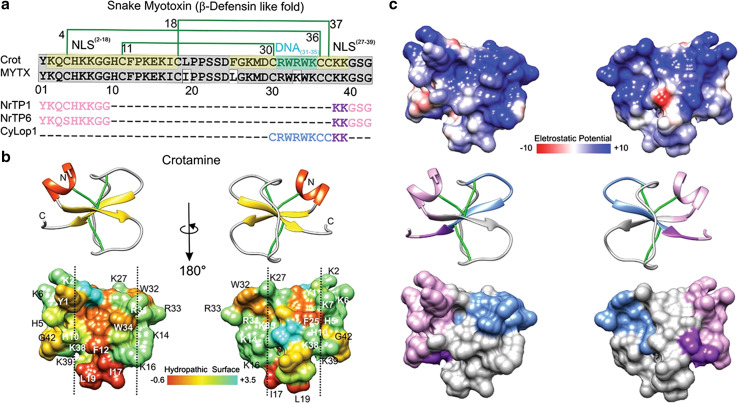
Fig. 3.
Crotamine, myotoxin a and peptides derived thereof a. Mature primary sequence of crotamine (UniProt structure identifier Q9PWF3) is aligned with MYTX (UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot sequence P01476.1) and three crotamine-derived CPPs. The disulfide bridge pattern is shown in green lines. In gray, conserved sequences between crotamine and MYTX, in pea-green basic stretches forming the putative NLS2–18 and NLS27–39, in turquoise, putative DNA interacting residues (DNA31–35); in pink and purple, nuclear localization signals that, combined, generate NrTP-1 [46] and NrTP-6 [101] (purple indicates the conserved sequence between the three peptides); in blue, remaining CyLop-1 sequence [48]. b, c The secondary structure and tridimensional surfaces of crotamine are shown for two opposite surfaces, in b the distribution of hydrophobic and hydrophilic sequences is shown [102], having been based on UniProt structure 1Z99 [102]. The vertical dashed line delimitates hydrophobic surfaces of the toxin. The dipole moment was calculated using default parameters with the Protein Dipole Moments Server [103], based on Peigneur et al. [41] and Sabatier and De Waard [104]. In c, the distribution of electrostatic charge is shown. Electrostatic surface colored according to Coulombic electrostatic potential, e = 4r, thresholds ± 5 kcal mol−1 e−1 at 298 K. Hydrophobicity surface colored following the Hessa and von Heijne hydropathic scale thresholds (dark orange most hydrophobic; white 0; aquamarine most hydrophilic) as described by Hessa et al. [44]. Secondary structure: beta-strand depicted in yellow, alpha-helix in red, coil in pale gray and disulfide bonds, in green. Molecular graphics and analyses for three-dimensional structures were performed with the UCSF Chimera package software [100]