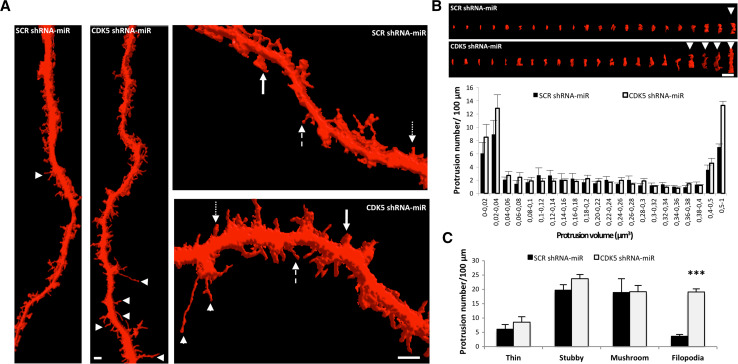
Fig. 4.
CDK5 silencing increases filopodia protrusion. a 3D rendering of dendrites is shown for Scr and CDK5 shRNA-miR neurons. Scale bar 2 μm. The dendrites from Scr neurons have different types of spines, including mushroom (arrows), stubby (dotted arrow), and thin (dashed arrow), constituting the population of mature spines. In contrast, although CDK5 shRNA-miR neurons have different types of mature spines, they generate long protrusions without a distinguishable head corresponding to filopodia protrusions (arrowhead). b Protrusion volume distribution for each condition shows protrusion size categories. CDK5 shRNA-miR increased protrusions with a larger size than that in controls, corresponding to filopodia or intermediates (arrowhead). c The graph shows the different types of spines found in 100-μm dendritic lengths (ten neurons from three independent experiments per condition). Representative data for b and c are presented as the mean ± SEM of n = 4. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001; Student’s t test