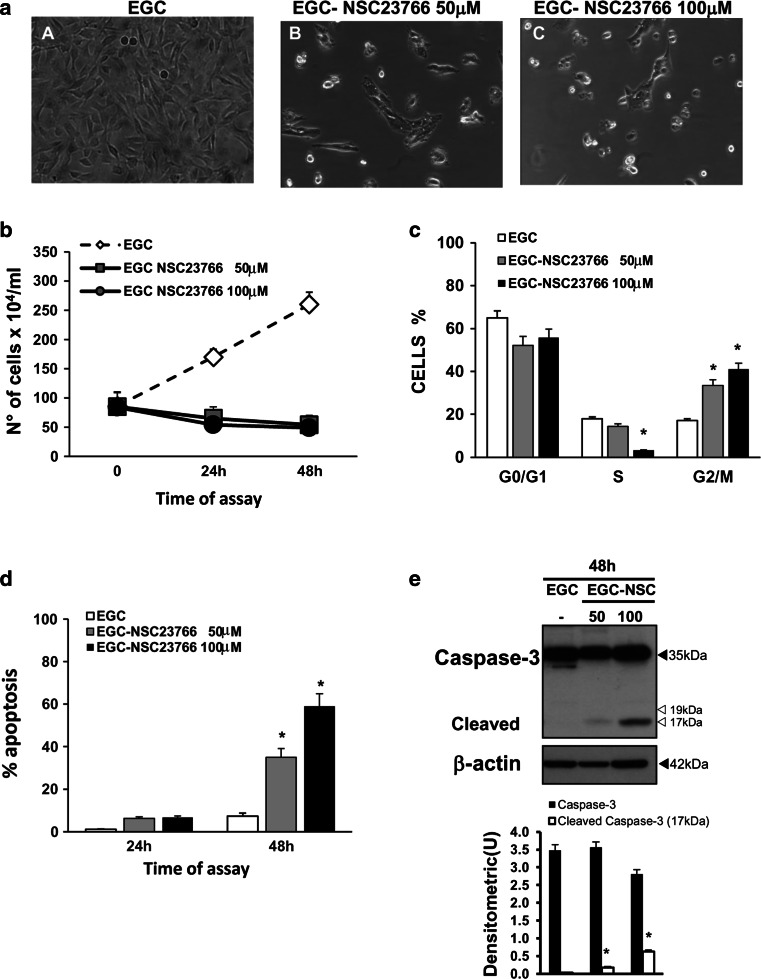
Fig. 12.
Pharmacological inhibition of Rac1 in EGCs. a Effect of Rac1 inhibitor on cell rounding. At the time indicated, control EGCs at 24 h (image A), EGCs treated with 50 μM NSC23766 for 24 h (image B), and EGCs treated with 100 μM NSC23766 for 24 h (image C) were analysed by microscopy, and images were captured. Images of one experiment representative of three independent experiments are shown. b–d Control EGCs and EGCs treated with 50 or 100 μM NSC23766 were recovered at 24 and 48 h and b the total cell number was determined by trypan blue; c the cell percentages in the cell-cycle phases G0/G1, S and G2/M were determined by flow cytometry with ModFit software and d apoptosis was measured by evaluating the percentage of hypodiploid nuclei via flow cytometry. For all the graphs, data are the mean ± standard deviation of three experiments performed in triplicate. *P < 0.01 NSC23766-treated EGCs versus control EGCs. e Lysates from control EGCs and EGCs treated with 50 or 100 μM NSC23766 prepared at 48 h were subjected to SDS-PAGE and probed with anti-caspase-3 then stripped and probed with anti-β-actin. The graphs represent the densitometric analysis of each protein relative to β-actin. *P < 0.01 NSC23766-treated EGCs versus control EGCs