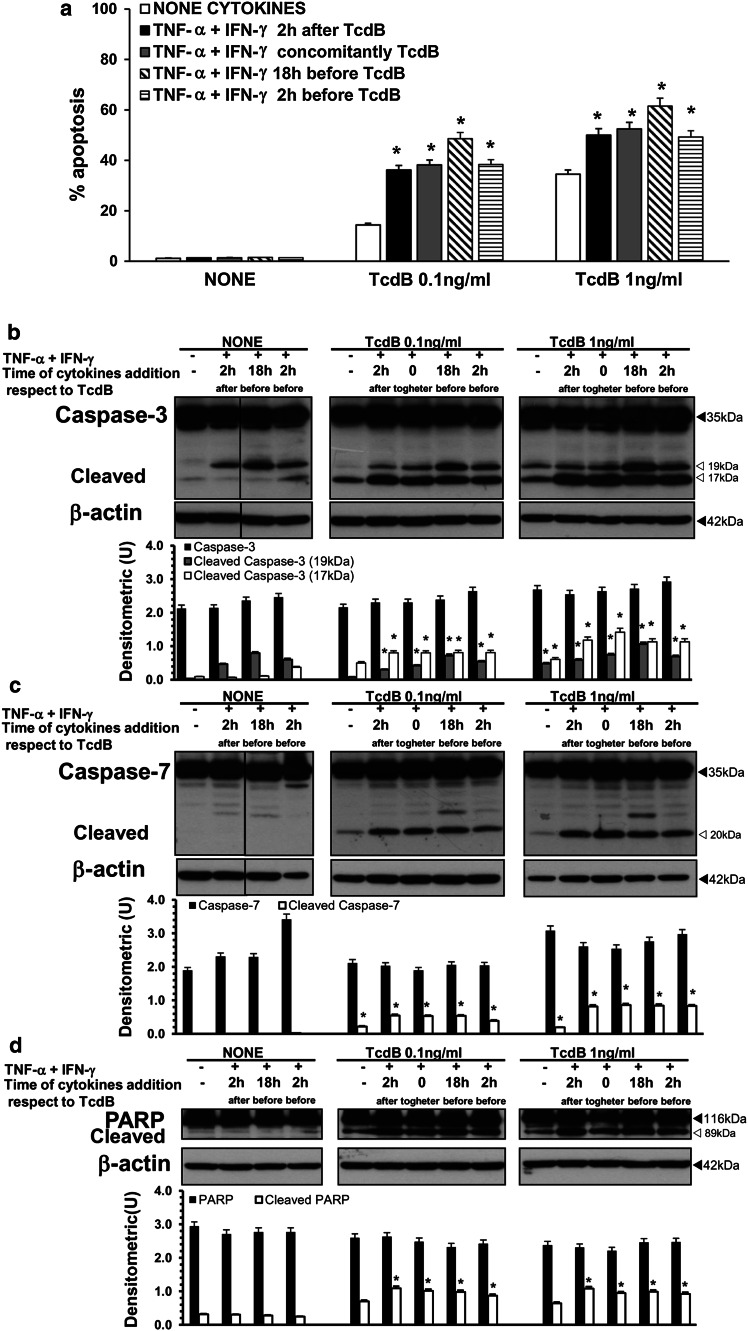
Fig. 15.
TNF-α plus IFN-γ added to EGCs at various times with respect to TcdB treatment increase EGC susceptibility to TcdB-induced apoptosis via caspase-3, caspase-7 and PARP activation. EGCs were treated with 50 ng/ml TNF-α plus 50 ng/ml IFN-γ: (1) 2 h after, (2) concomitantly, (3) 18 h before, and (4) 2 h before TcdB treatment (0.1, 1 ng/ml). EGCs not treated with TcdB but treated with 50 ng/ml TNF-α plus 50 ng/ml IFN-γ in the same conditions were control EGCs. Cells from all the experimental conditions were recovered at 24 h after being treated or not with TcdB for the evaluation of apoptosis (a) and the preparation of lysates, SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis (b–d). a Apoptosis was determined at 24 h by measuring the percentage of hypodiploid nuclei via flow cytometry. The data are the mean ± standard deviation of six experiments performed in triplicate. *P < 0.01 TcdB-treated, stimulated EGCs versus TcdB-treated, non-stimulated EGCs. For Western blot analysis the filters were probed with: b anti-caspase-3 then stripped and probed with anti-β-actin; c anti-caspase-7 then stripped and probed with anti-β-actin; d anti-PARP then stripped and probed with anti-β-actin. The vertical lines in the blots indicate repositioned gel lanes. The graphs represent the densitometric analysis of each protein relative to β-actin. *P < 0.01 TcdB-treated, stimulated EGCs versus TcdB-treated, non-stimulated EGCs