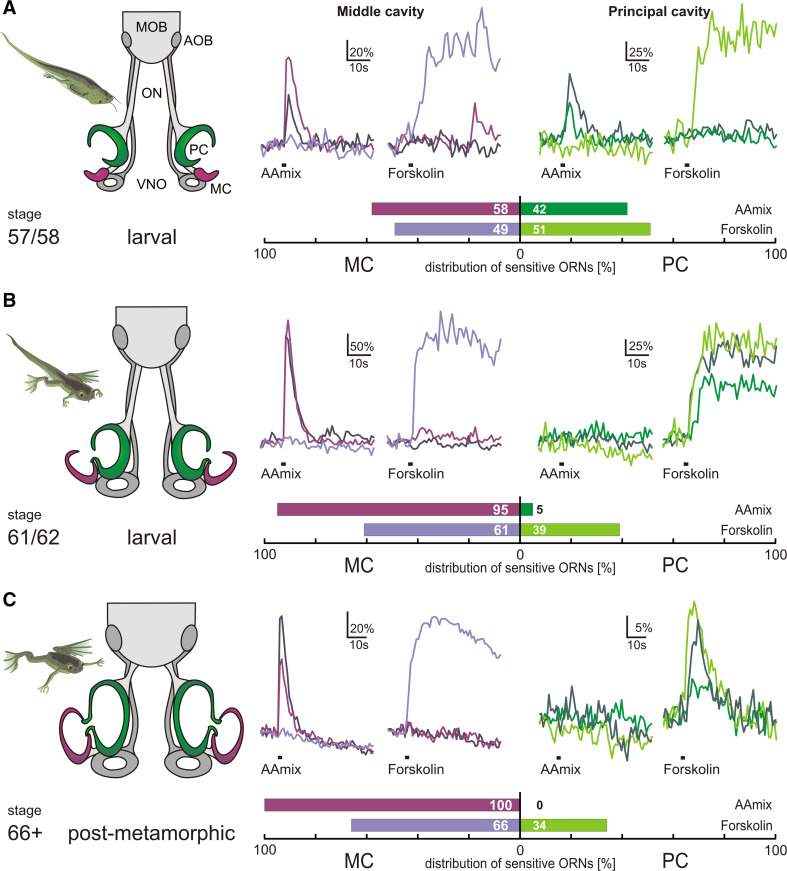
Fig. 1.
Metamorphotic shift of the sensitivity to amino acid odors from the principal cavity to the newly formed middle cavity. The metamorphotic stages examined for Xenopus laevis are visualized as schematic drawings to the left. Calcium transients induced by amino acid mix (100 µM) and forskolin (50 µM) in acute slices are represented as ∆F/F, with responses of three representative ORNs overlaid for each stimulus (amino acid mix, forskolin) and olfactory cavity (middle and principal cavity). Shades of magenta are used for traces of middle cavity neurons, whereas shades of green are used for neurons located in the principal cavity. Within one panel, traces with the same color originate from the same neuron. The relative abundance of neurons analyzed is given as horizontal bar graphs below the representative traces; dark shades, amino acid responses; light shades, forskolin responses. a Late prometamorphotic stage, note the forming MC (magenta), the PC (green) and the vomeronasal organ (VNO; gray). At this stage, ORNs of the MC already show responsiveness to amino acid odors and forskolin, while the PC still shows responses characteristic of the PC of premetamorphotic larvae (see [10]). Amino acid odor and forskolin-sensitive ORNs are almost equally distributed between the epithelia of the two cavities. b Mid-metamorphosis stage, MC (magenta), PC (green) and VNO (gray) have grown in size. In this stage, the responsiveness to amino acid odors has almost completely shifted to the epithelium of the MC (see bar diagram). Forskolin-sensitive ORNs still coexist in both the epithelia of the MC and PC. c Post-metamorphotic froglet: all three epithelia have further grown in size and the olfactory nerve (ON) has become shorter. The responsiveness to amino acid odors has completely shifted to the epithelium of the MC. Forskolin-sensitive ORNs continue to coexist in both the epithelia of the MC and PC (see bar diagram). AOB accessory olfactory bulb, MOB main olfactory bulb, ON olfactory nerve, ORNs olfactory receptor neurons, PC principal cavity, MC middle cavity, VNO vomeronasal organ, AAmix amino acid mixture