Fig. 6.
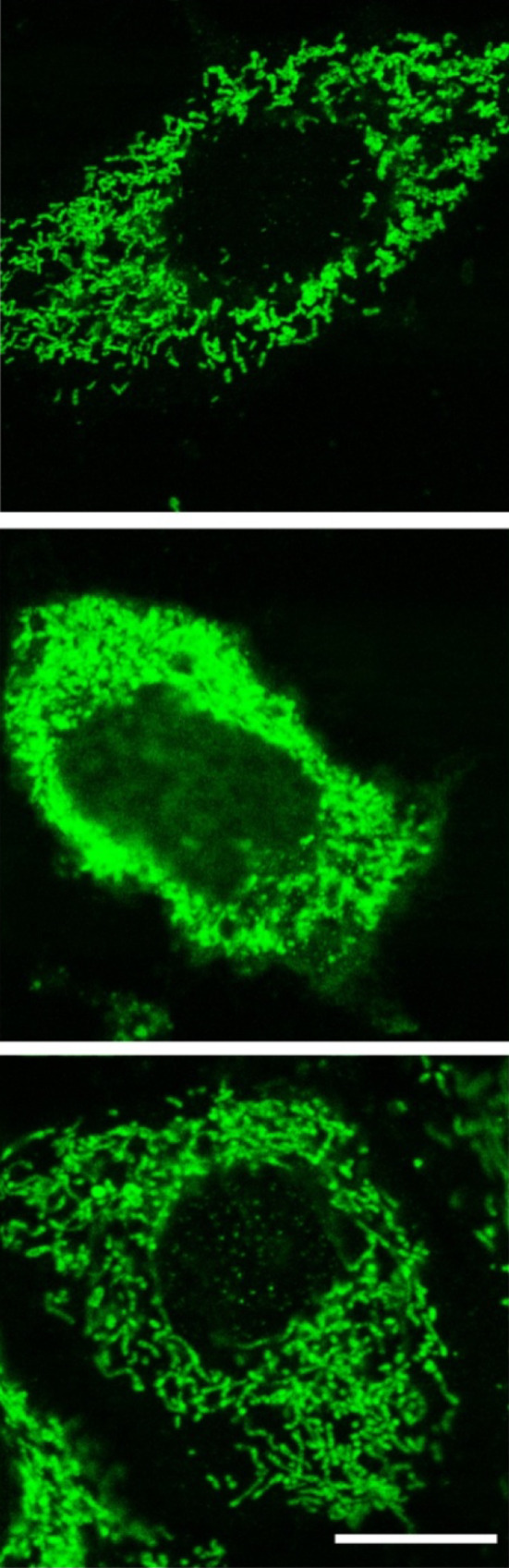
The induction of cellular apoptosis after exposure to an oxidant involves the release of cytochrome c from damaged mitochondria with the subsequent activation of caspases leading to programmed cell death. This figure illustrates the localizations of cytochrome c in the mitochondria of astrocytes not exposed to an oxidant (top); middle after 90 min exposure to H2O2; bottom after exposure to H2O2 plus melatonin. Clearly, H2O2 treatment caused a massive release of cytochrome c into the cytosol and much less into the nucleus with melatonin almost totally preventing this escape. The release of cytochrome c occurred simultaneously with retraction of cell processes, shrinkage of the cells and an irregular plasma membrane. Cytochrome c was detected using immunocytochemistry and laser scanning confocal microscopy. Bar 10 µM.
Reprinted with permission from Jou et al. [95]
