Extended Data Fig. 6 |. Microbial associations with immune-related toxicity are confirmed by whole metagenomic sequencing.
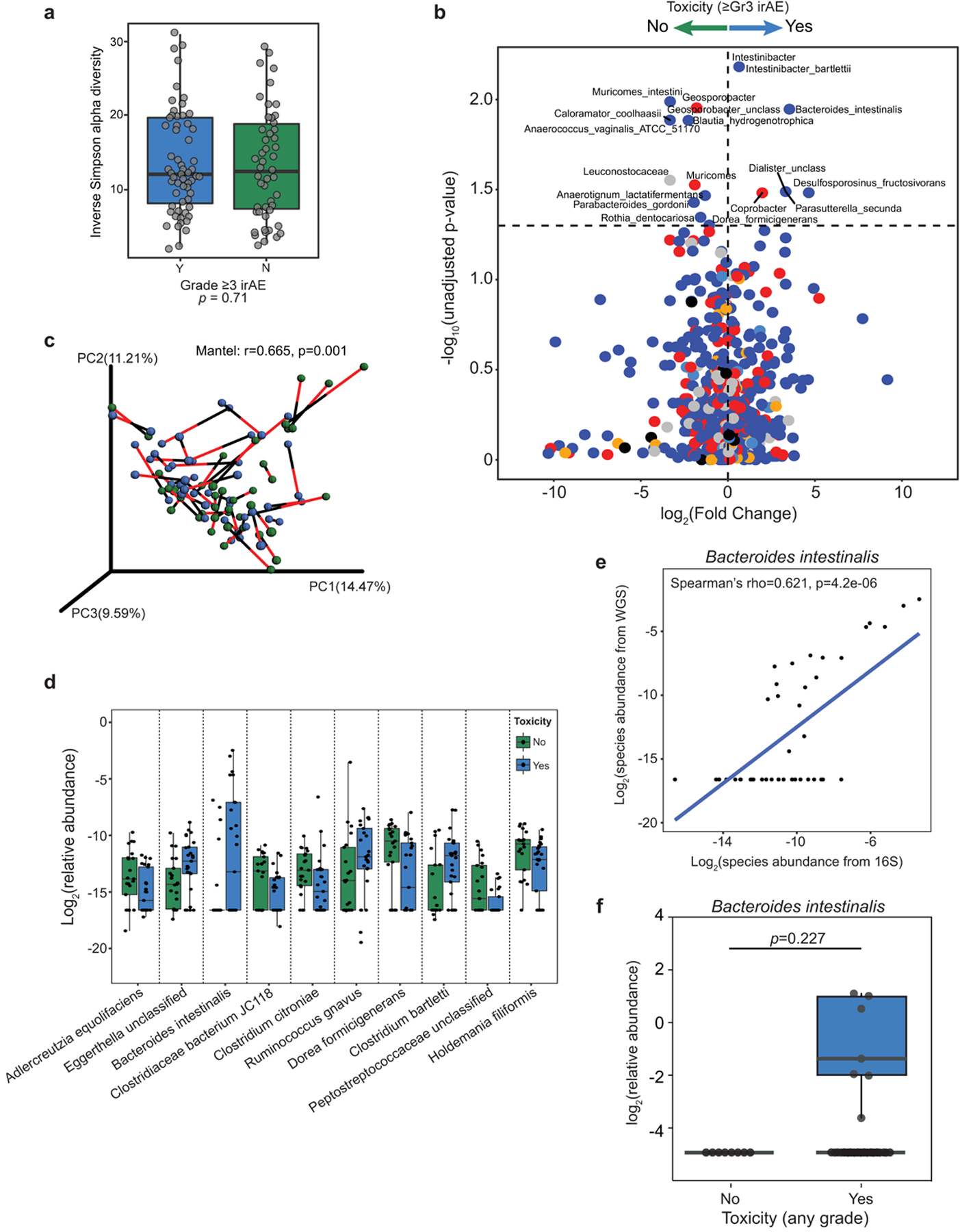
a, Inverse Simpson alpha diversity from 16S sequencing of baseline fecal microbiota in CICB-treated patients (n = 54) was not associated with subsequent development of high-grade immune-related adverse events (irAE). Mann-Whitney test (p = 0.71). b, Volcano plot of pairwise comparisons of bacterial taxa (at all levels) dichotomized by experience of high-grade (≥Grade 3) immune-related adverse events (n = 54 patients) using Mann-Whitney tests applied to 1000 permutations of differential bacterial abundance. Unadjusted p-values shown, adjusted values in supplemental tables 5 and 8. c, Procrustes analysis demonstrating high concordance between taxonomic identification using either 16S or WMS methods (Mantel: r=0.665, p = 0.001). d, Confirmation of bacterial candidate associations with toxicity using WMS (≥ Gr3 irAE: n = 25 Yes, n = 21 No). Significant associations existed for Bacteroides intestinalis (p = 0.032) and Dorea formicigenerans (p = 0.020) all other associations were non-significant. e, A strong positive correlation was observed between abundance of Bacteroides intestinalis quantified using 16S versus WMS (Spearman’s rho=0.62, p = 4.2e-6). f, Box-whisker plot of relative abundance of Bacteroides intestinalis in the combined McGill/University of Toronto cohort of melanoma patients treated with immune checkpoint blockade demonstrating identification of this species exclusively in patients developing irAE (≥Gr1 n = 37 Yes, n = 8 No; One-tailed Mann Whitney test p = 0.2269). Box plots present the median bar with the box bounding interquartile range (IQR) and whiskers to the most extreme point within 1.5 × IQR. All tests are two sided unless otherwise specified.
