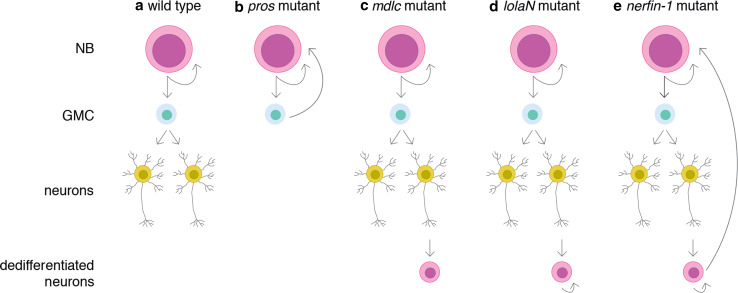
Fig. 1.
Dedifferentiation in the Drosophila brain. a Wild-type neuroblasts (NBs) divide asymmetrically to self-renew and to generate a smaller daughter cell, the ganglion mother cell (GMC) that divide once to generate differentiated neurons. b pros mutant GMCs are unable to differentiate and re-acquire a NB fate [6]. c mdlc mutant neurons express NB markers but are unable to proliferate [20]. d lolaN mutant post-mitotic neurons in the optic lobes dedifferentiate and re-enter the cell cycle [34]. e Nerfin-1-deficient post-mitotic neurons dedifferentiate, re-enter the cell cycle and grow back to give rise to a fully functional NB [32]