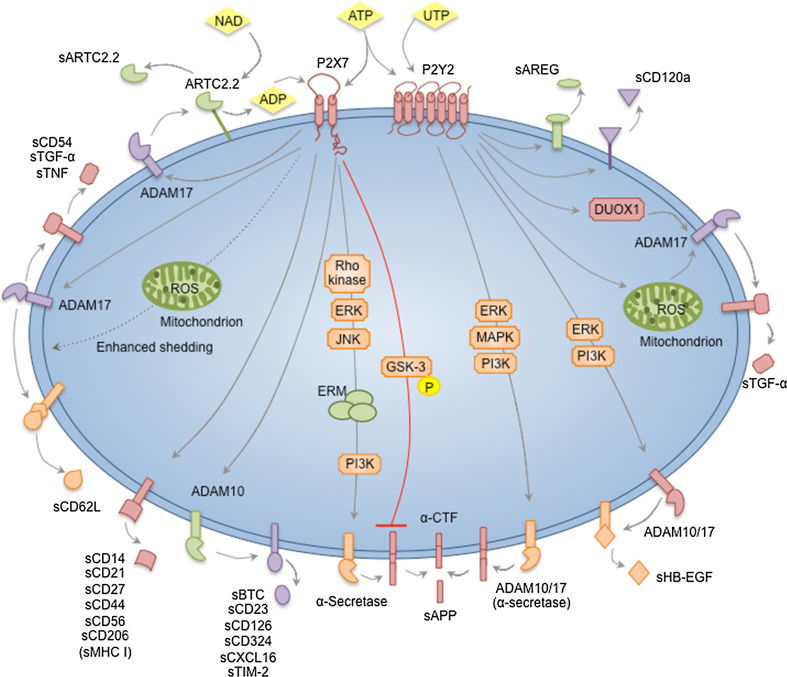
Fig. 1.
Nucleotide-induced ectodomain shedding. ATP activates P2X7 receptors. NAD can also activate P2X7 via the ADP-ribosyltransferase, ARTC2.2. P2X7 activation can stimulate ADAM10 to induce the shedding of BTC, CD23, CD126, CD324, CXCL16 and TIM-2. P2X7 activation can stimulate ADAM17 to induce the shedding of ARTC2.2, CD54, CD62L, TGF-α and TNF. P2X7-induced shedding of CD62L can be enhanced by mitochondrial ROS formation. P2X7 activation can stimulate α-secretase to induce APP shedding via an intracellular signalling cascade involving Rho-kinase, ERK, JNK, ERM and PI3K. An opposing role for P2X7 in APP processing is also suggested, whereby APP processing is inhibited by GSK-3 downstream of P2X7 activation. Finally, P2X7 activation can induce the shedding of CD14, CD21, CD27, CD44, CD56, CD206, and possibly MHC class I molecules, but the sheddases involved remain unknown. ATP and UTP can stimulate P2Y2 receptors. P2Y2 activation can stimulate ADAM17, via DUOX1 and mitochondrial ROS generating pathways, to induce the shedding of TGF-α. P2Y2 activation can stimulate ADAM10 and ADAM17 to induce HB-EGF shedding via an intracellular signalling cascade involving ERK and PI3K. P2Y2 activation can also stimulate ADAM10 and ADAM17, which serve as α-secretases, to induce APP shedding via an intracellular signalling cascade involving ERK, MAPK and PI3K. Finally, P2Y2 activation (or possibly activation of other P2Y receptors) can induce the shedding of AREG and CD120a, but the sheddases involved remain unknown. ADAM a disintegrin and metalloprotease, ADP adenosine 5′-diphosphate, APP amyloid precursor protein, AREG amphiregulin, ATP adenosine 5′-triphosphate, BTC betacellulin, CD21 complement receptor 2, CD23 IgE receptor, CD27 tumour necrosis factor receptor, CD44 hyaluronic acid receptor, CD54 intercellular adhesion molecule-1, CD56 neural cell adhesion molecule, CD62L l-selectin, CD120a tumour necrosis factor receptor 1, CD126 interleukin-6 receptor, CD324 E-cadherin, CTF carboxyl-terminal fragment, DUOX1 NADPH oxidase homolog dual oxidase 1, ERK extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ERM ezrin radixin moesin, GSK glycogen synthase kinase, HB-EGF heparin-binding-epidermal growth factor, JNK c-Jun N-terminal kinase, MHC major histocompatibility complex, NAD nicotinamide adenine nucleotide, PI3K phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase, ROS reactive oxygen species, TIM T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain, TGF transforming growth factor, TNF tumour necrosis factor, UTP uridine 5′-triphosphate