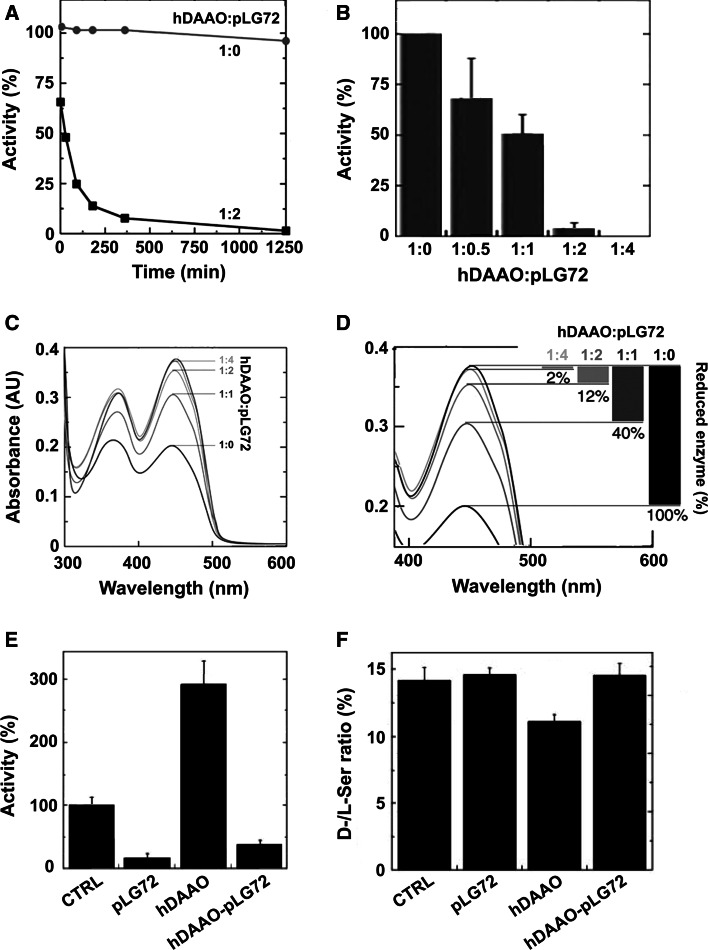
Fig. 3.
Effect of pLG72 binding on hDAAO activity and d-serine cellular concentration [16]. a Effect of pLG72 on the time course of hDAAO enzymatic activity. A slow inactivation is evident in the presence of a twofold molar excess of pLG72 (filled squares) in buffer containing 0.06 % NLS. b Effect of pLG72 on hDAAO activity following 30 min of incubation of a fixed amount of hDAAO (0.1 nmol/mL) with increasing amounts of pLG72. c, d Effect of pLG72 on the substrate-induced FAD reduction in hDAAO. Flavin reduction was monitored spectroscopically in anaerobic conditions by detecting the change in absorbance at 455 nm after the addition of 1 mM d-serine to hDAAO solutions (15 μM) containing free FAD and different amounts of pLG72 (hDAAO:pLG72 molar ratio 1:0, 1:1, 1:2, 1:4). d Spectral changes at 455 nm at higher magnification. The percentage of hDAAO flavin reduction (i.e., the amount of active hDAAO) at different concentrations of pLG72 is reported on the right. e DAAO activity was assayed in control U87 cells (CTRL, fixed as 100 %) and in the same transfected cells expressing hDAAO, pLG72 or both proteins. A significant increase in activity was evident in hDAAO transfected cells with respect to the control (p = 0.012) while a decrease was observed when pLG72 was overexpressed. f d-Serine concentration in control and transfected U87 cell extracts. d- and l-serine cellular content was determined by HPLC analysis. A significant decrease in the d-/l-serine ratio is apparent in hDAAO transfected cells with respect to controls (p = 0.004) while no difference is observed in pLG72 and hDAAO–pLG72 co-transfected cells