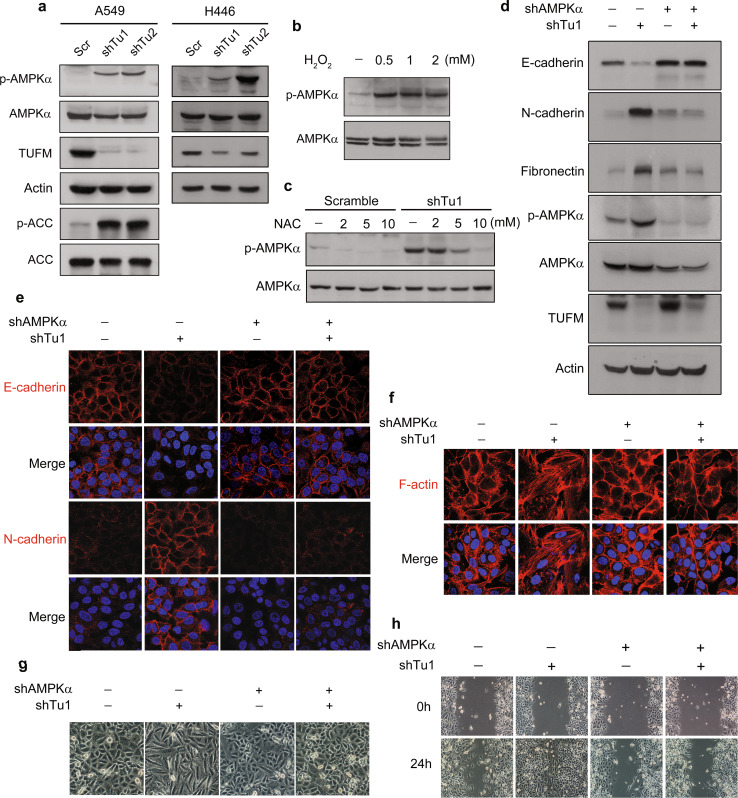
Fig. 6.
AMPK activation is essential for EMT induction by TUFM knockdown. a TUFM-knockdown-induced AMPK activation was assessed by examining the levels of p-AMPK (T172) and p-ACC in A549 and H446 cells by immunoblotting. b A549 cells were treated with H2O2 at the indicated concentrations for 2 h and the expression levels of AMPK and p-AMPK (T172) were determined by immunoblotting. c Effect of NAC treatment (2 h) on AMPK and p-AMPK (T172) levels in control and TUFM-knockdown A549 cells. d–g Inhibition of AMPK activation by AMPKα knockdown suppressed the induction of EMT by TUFM knockdown, as determined by immunoblotting (d) and immunofluorescent staining of EMT marker proteins (e), immunofluorescent staining of F-actin (f), and cell morphologic changes (g). h Cell migration of control and TUFM-knockdown A549 cells with or without AMPKα knockdown was examined by the wound-healing assay