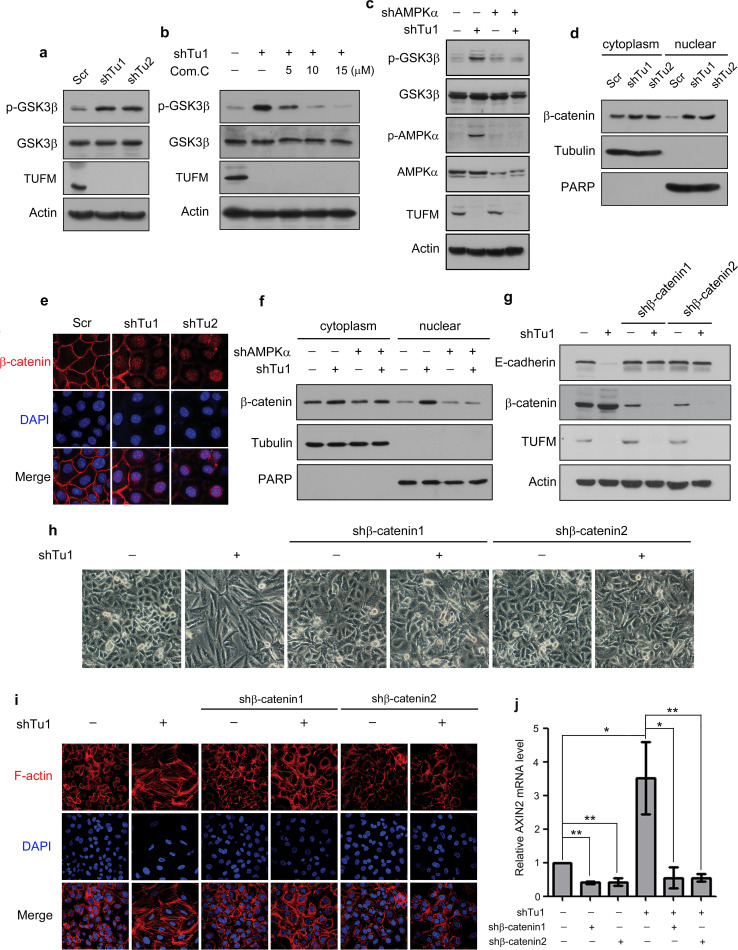
Fig. 7.
TUFM knockdown activates the AMPK/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. a The effect of TUFM knockdown on GSK3β phosphorylation (S9) in A549 cells was examined by immunoblotting. b The effect of various doses of Compound C (24 h) on the levels of phosphorylated GSK3β (S9) in control and TUFM-knockdown A549 cells was examined by immunoblotting. c Inhibition of AMPK activation by AMPKα knockdown inhibited GSK3β phosphorylation induced by TUFM knockdown, as detected by immunoblotting. d Isolation of the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of control and TUFM-knockdown cells. Tubulin and PARP were used as loading controls for the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, respectively. e Immunofluorescent staining of β-catenin in control and TUFM-knockdown cells. f Cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of the indicated cells were isolated. Tubulin and PARP were used as loading controls for the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, respectively. g–i shRNA targeting β-catenin suppressed TUFM-knockdown-induced EMT, as assessed by the level of E-cadherin (g), cell morphologic changes (h), and F-actin rearrangement (i). j Relative mRNA levels of Axin2 in the indicated cells were quantified using real-time PCR