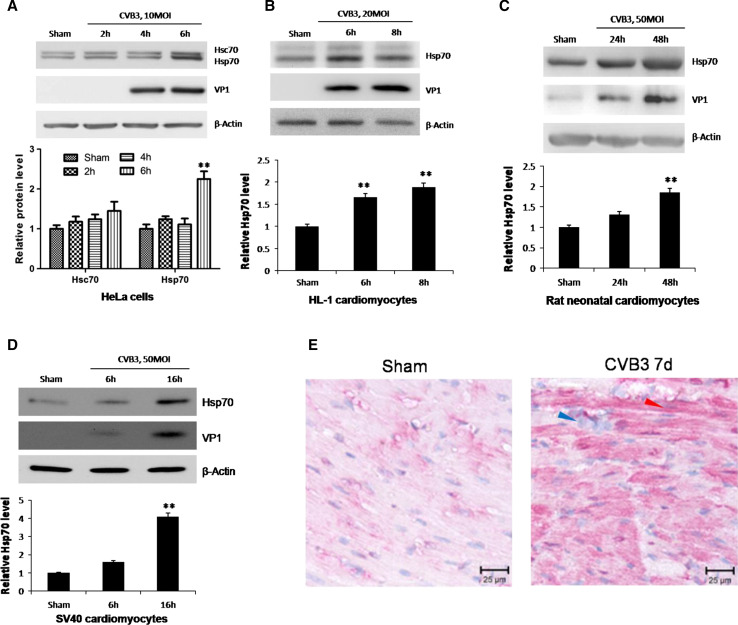
Fig. 1.
CVB3 infection induces upregulation of Hsp70 both in vitro and in vivo. HeLa cells (a), HL-1 cardiomyocytes (b), neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (c) and SV40 human cardiomyocytes (d) were infected by CVB3 at 10 MOI, 20 MOI, 50 MOI and 50 MOI, respectively. Cell lysates were collected for Western blot to detect the protein levels of Hsp70. Hsc70, a constitutively expressed cognate of Hsp70, was detected by a monoclonal mouse anti-Hsp70/Hsc70 antibody simultaneously (a). β-actin was detected as a loading control and cells treated with PBS (Sham) were used as a negative control. Band intensities were quantified using the ImageJ program, normalized against β-actin and shown as mean ± SD (n = 3) (see lower panels of a, b, c and d; **p < 0.01). e 4-week old A/J mice were infected with 105 pfu of CVB3 or sham-infected with saline. At 4 days pi, mice were killed and the ventricular wall tissue was fixed and subjected to immunohistochemical staining using an anti-Hsp70 antibody. The blue arrow indicates immune cell nuclei in the myocardium. The red arrow indicates a typical cardiomyocyte with Hsp70 protein upregulation (red)