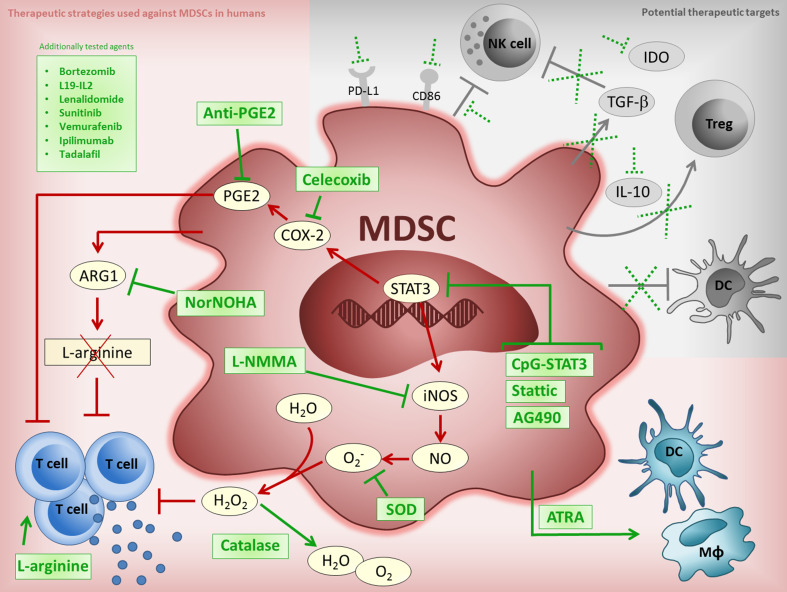
Fig. 1.
Current and potential MDSC targeting strategies. Figure shows the currently tested approaches against human MDSC (red shaded background) and potential therapeutic targets (grey shaded background). Red and grey lines indicate MDSC suppressive pathways, green lines show where therapeutic agents may interfere with these pathways, broken green lines indicate where potential therapeutic agents may act against MDSC suppressive mechanisms, green boxes list previously tested drugs which can interfere with MDSCs. The overlapping suppressive pathway involving STAT3/COX-2/PGE2 can be targeted upstream by STAT3 inhibitors (CpG-STAT3 [53], Stattic [47], AG490 [17]), or further downstream by agents acting against the COX-2 enzyme (Celecoxib) [17] or its product, PGE2 (anti-PGE2 [17]). MDSC depletion of l-arginine via elevated ARG1 levels can result in T cell dysfunction. This may be counteracted by inhibitors of ARG1 (NorNOHA) [17, 53, 109] or by arginine supplementation [97]. ATRA [92, 104, 110] can act to differentiate MDSCs into to non-suppressive cells. Production of reactive oxygen species is a further MDSC mechanism of suppression which can be inhibited upstream via STAT3, by iNOS inhibitors (L-NMMA) [109] or through SOD [17, 110] and catalase [17, 97, 110] directly. Additional agents, such as kinase inhibitors (sunitinib [50, 94, 97, 98], vemurafenib [32]), immunotherapeutics (L19-IL2 [101], ipilimumab [66, 99, 115]) and yet other agents (bortezomib [90, 96, 116], lenalidomide [90, 93, 116], tadalafil [102, 103]) have also been shown to be active against MDSCs. Suppressive mechanisms employed by MDSCs that remain to be exploited for therapy include their effect on DCs, NK cells, Treg induction and via IDO, IL-10, TGF-β, PD-L1 and CD86. ARG1 arginase 1, ATRA all-transretinoic acid, COX-2 cyclooxygenase-2, CpG cytosine-phosphate-guanine oligodeoxynucleotide, DC dendritic cell, IDO indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, iNOS inducible nitric oxide synthase, L19-IL2 L19-IL2 monoclonal antibody-cytokine fusion protein, L-NMMA NG-Methyl-l-arginine, MDSC myeloid-derived suppressor cell, MΦ macrophage, NK natural killer cell, Nor-NOHA N(omega)-hydroxy-nor-l-arginine, PD-L1 programmed death-ligand 1, PGE2 prostaglandin E2, SOD superoxide dismutase, STAT3 signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, TGF-β transforming growth factor beta, Treg regulatory T cell