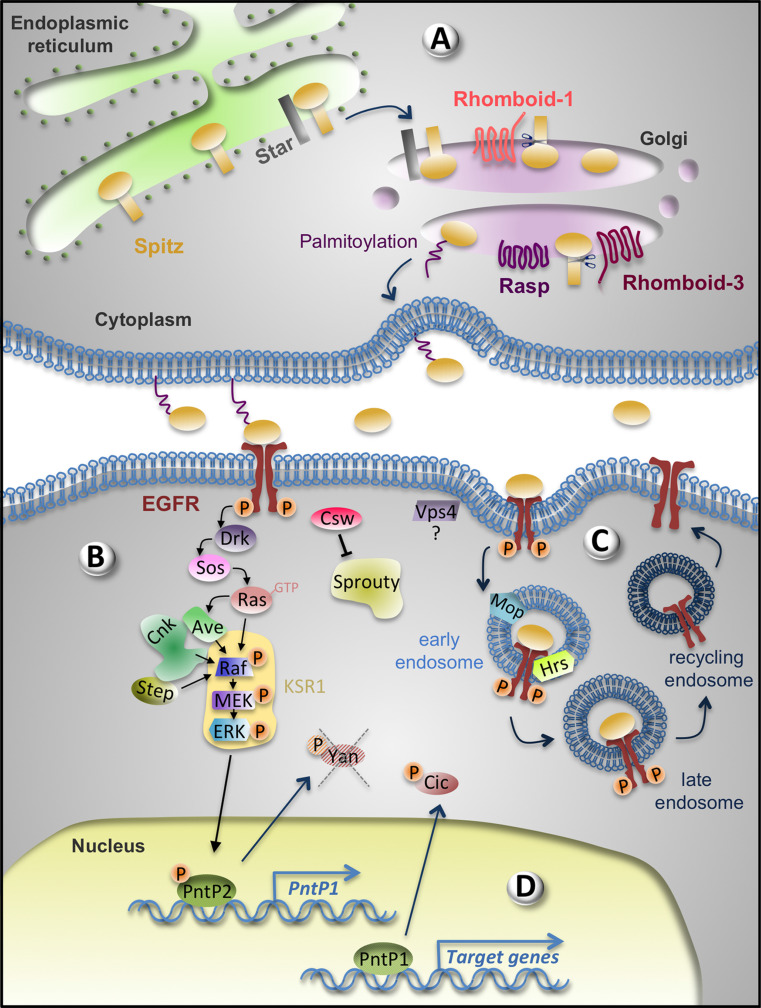
Fig. 1.
Positive regulators of the EGFR signalling pathway. a The ligand Spitz is produced in the sending cell. Spitz is retained in the ER until Star promotes its translocation to the Golgi apparatus where it is cleaved by Rhomboid-1 or 3 making it soluble. Palmitoylation by Rasp promotes Spitz tethering to the plasma membrane to increase concentration at secreting sites. Both unpalmitoylated and palmitoylated Spitz can be released. b In the receiving cell, upon Spitz binding, the EGFR dimerizes leading to its autophosphorylation and activation of the canonical Drk/Sos/Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway. KSR1, a scaffolding protein, brings members of the pathway in close proximity. CNK interaction with Ave and Step contributes also to Raf activation. The inhibitor Sprouty is dephosphorylated, and thus inactivated by the phosphatase Csw. c Vps4, Mop and Hrs are also positive regulators. Mop and Hrs participate in EGFR endocytosis. Recycling of the EGFR to the plasma membrane is important to maintain active signalling. d In the nucleus, phosphorylated ERK triggers the exit of the transcriptional repressor Yan and phosphorylates PntP2, which activates PntP1 transcription. When sufficient levels of PntP1 are reached, the various target genes of the EGFR signalling pathway are transcribed. Phosphorylated ERK also phosphorylates the transcriptional repressor Cic, which results in its export out of the nucleus and the subsequent transcriptional activation of EGFR signalling target genes