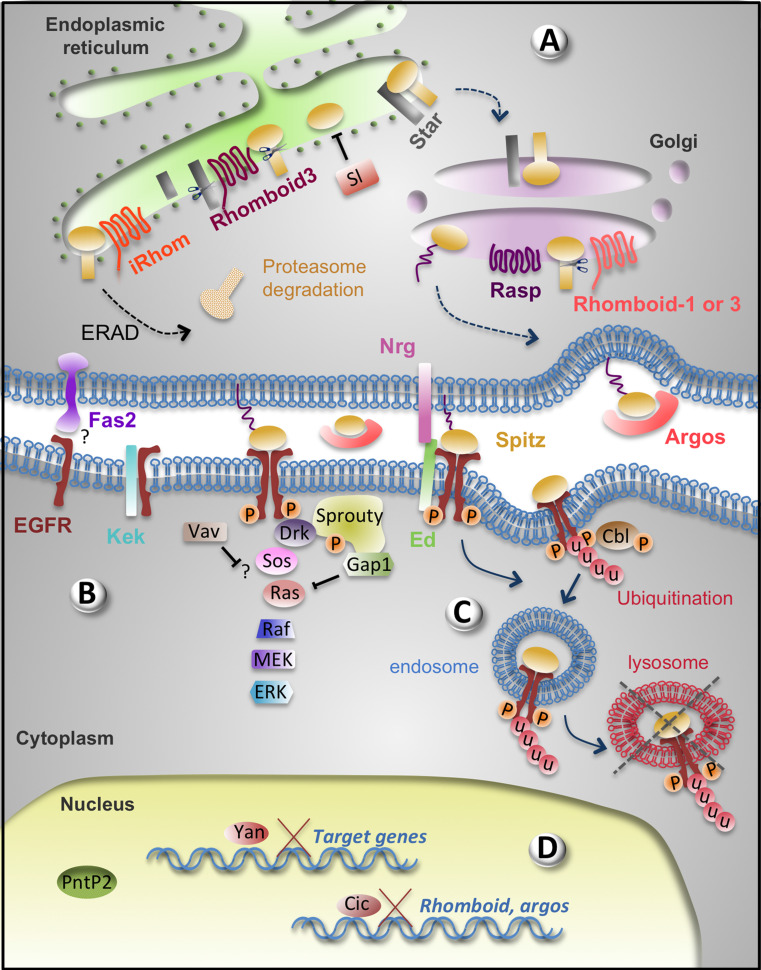
Fig. 3.
Negative regulators of the EGFR signalling pathway. a In the ER of the signalling cell, Rhomboid-3 cleaves both the chaperone Star, so less Spitz can be transferred to the Golgi, and Spitz itself. Cleaved Spitz is retained in the ER by Sl. iRhom promotes ERAD in which Spitz is transferred to the cytoplasm and degraded by the proteasome. Thus, only the Spitz molecules that encounter Star, escape cleavage and ERAD can be transferred to the Golgi and secreted. b At the plasma membrane of the receiving cell, EGFR is inhibited non-autonomously by Fas2 by an unknown mechanism, and autonomously by Kek and Ed. Nrg contributes non-cell autonomously to EGFR inhibition by Ed. In the cytoplasm, the MAPK cassette is inhibited by Gap1 (inactivating Ras), Sprouty and Vav. Sprouty interacts with Drk, Gap1 and the plasma membrane. c Ed may contribute to EGFR inhibition via endocytosis. Cbl-mediated EGFR ubiquitination targets the receptor for endocytosis and lysosome degradation. d In the absence of phosphorylated ERK, the transcriptional repressors Yan and Cic repress EGFR pathway target genes and prevent the transcriptional activator Pnt from binding DNA