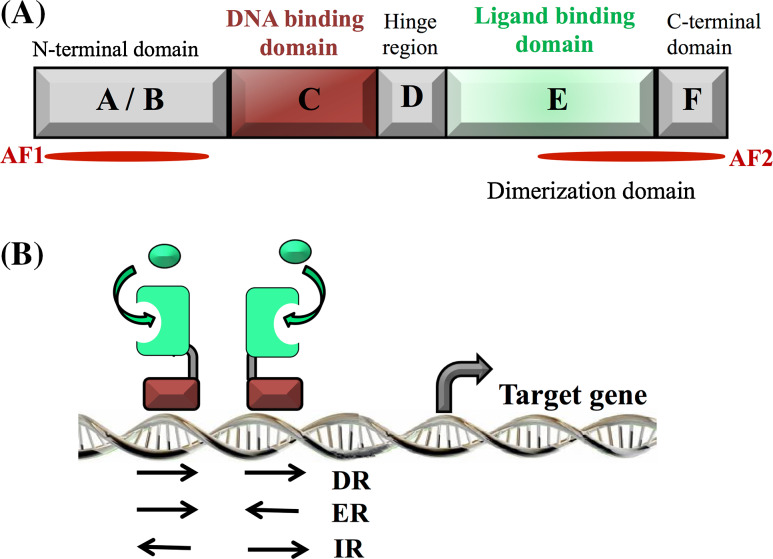
Fig. 1.
a Structural organization of nuclear receptors. The N-terminal domain contains the transactivation ligand-independent domain AF1. The DNA-binding domain (DBD) recognizes a specific sequence on the DNA called hormone responsive element (HRE). The ligand-binding domain, allowing the binding of the ligand(s), also contains the activation function 2 (AF2) and contributes to the dimerization interface. b Binding of nuclear receptors to the hormones responsive elements (HRE). Nuclear receptors bind as homodimer or heterodimer on specific sequences present on the DNA. HRE are composed of a repeat of one core motif that can be direct (DR), everted (ER), or inverted (IR), depending on the nuclear receptor subtype