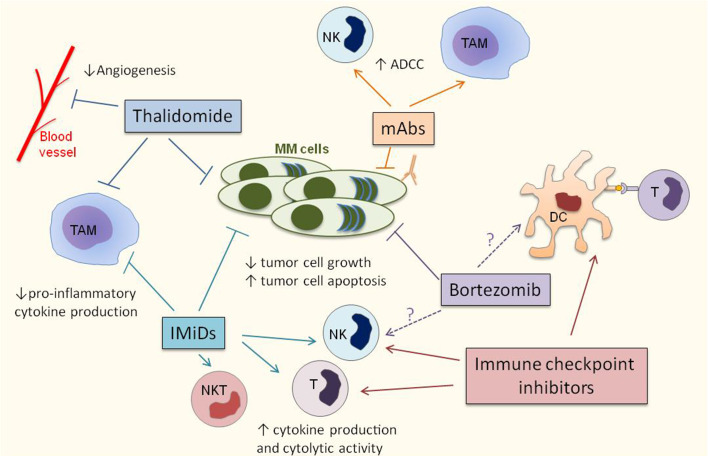
Fig. 2.
MM therapies modulate the immune microenvironment. Thalidomide, IMiDs, Bortezomib and monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) directly regulate tumor cell proliferation and survival. In addition, mAbs induce tumor cell death by triggering NK cell-mediated and tumor associated macrophage (TAM)-mediated antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Besides, thalidomide inhibits angiogenesis and both thalidomide and IMiDs decrease the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines by TAMs. IMiDs also promote the anti-MM activity of T cells, NK cells and NKT cells. The impact of bortezomib on anti-myeloma immune responses is unclear. Bortezomib may favor NK cell and dendritic cell (DC) functions by increasing the immunogenicity of MM cells; however toxic effects of bortezomib toward NK cells, DCs and T cells have also been described. Immune checkpoint inhibitors target the immune system to induce potent anti-tumor responses