Fig. 2.
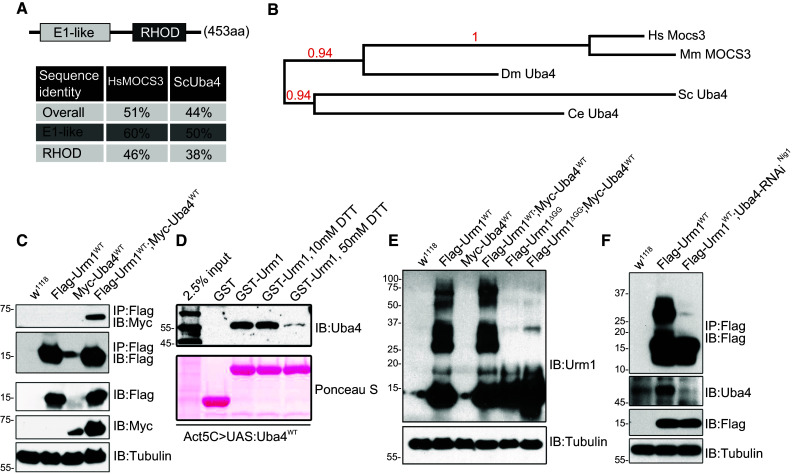
Drosophila Uba4 interacts with Urm1 and potentiates urmylation in vivo. a Schematic representation and evolutionary conservation of the Drosophila Uba4 homolog, CG13090. The Drosophila Uba4 is composed of an N-terminal E1-like domain and C-terminal Rhodanese homology domain (RHOD), similar to its human and yeast counterparts. Percent identity matrix was calculated using the online ClustalW2 tool developed by EMBL-EBI [68, 69]. b Phylogenetic analysis of the evolutionary conservation of Uba4, generated by utilizing the Phylogeny.fr platform [66, 67]. c Urm1 and Uba4 interacts in vivo. Immunoprecipitation of Flag-tagged Urm1 followed by immunoblotting with anti-Myc antibodies reveals that Flag-tagged Urm1 interacts with Myc-tagged Uba4. Proteins were overexpressed ubiquitously in adult flies using the GAL4/UAS system. d The interaction between Drosophila Urm1 and Uba4 is sensitive to reducing agents. A recombinant GST-tagged Urm1 protein was employed to pull down Uba4 from lysates of flies in which Uba4 is overexpressed under control of the Actin5C promotor (GAL4/UAS system). The addition of increasing concentrations of DTT abolishes the ability of Urm1 to bind Uba4. e Ectopic expression of Urm1 induces urmylation of multiple target proteins in adult flies, a process which is not observed when overexpressing a truncated version of Urm1 lacking the C-terminal GG motif used for conjugation (Urm1 ΔGG). f Urm1 conjugation to target proteins in adult flies is strongly reduced by RNAi-mediated knockdown of Uba4 expression
