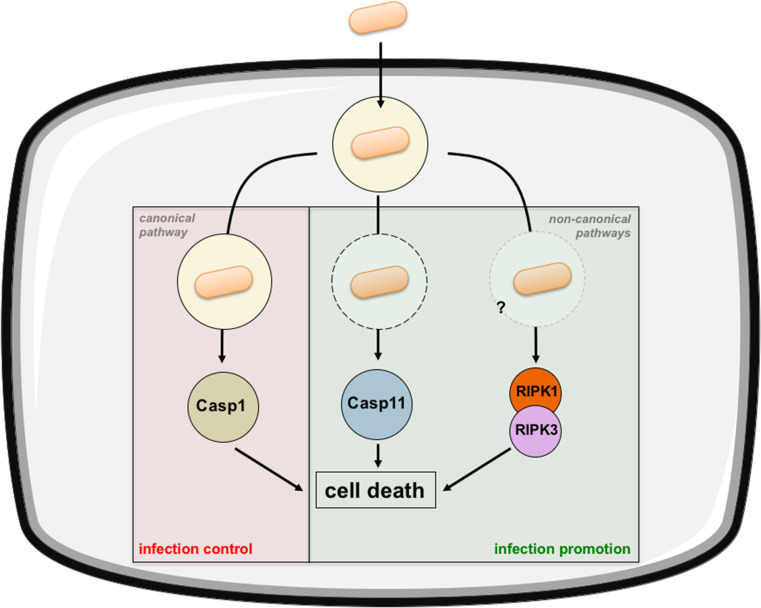
Fig. 3.
Salmonella-induced regulated cell death. Extracellular Salmonella is phagocytized leading to its internalization within a vacuole. From there, it will manipulate host cell metabolism thanks to secretion of virulence factors. It can induce cell death via the canonical pyroptotic pathway through caspase 1 activation. Cytoplasmic (extravacuolar) bacteria are also able to induce cell death in a noncanonical pathway by activating caspase 11. Finally, Salmonella can induce cell death via the RIPK1/RIPK3 pathway. Caspase 1-associated pyroptosis has a deleterious effect on bacteria limiting the infection whereas caspase 11-associated pyroptosis and RIPK1/RIPK3 necroptosis favor bacterial colonization