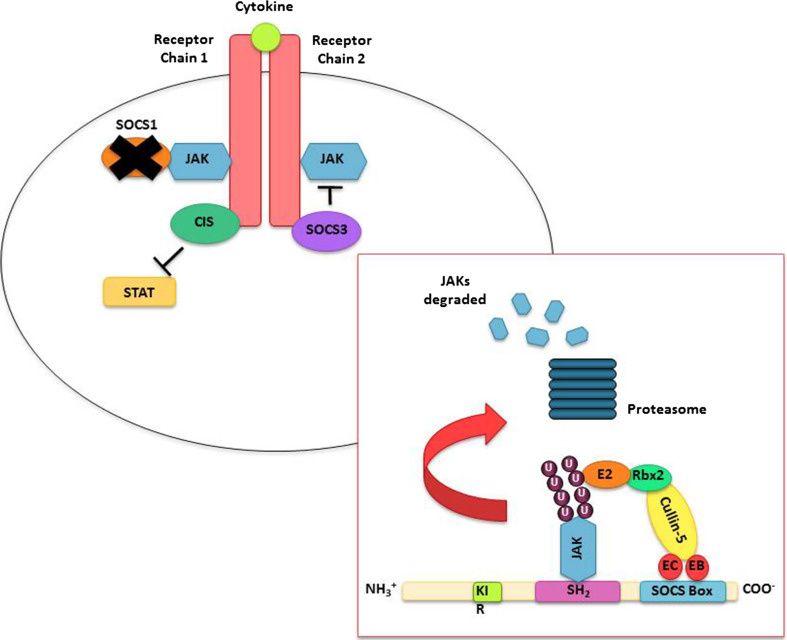
Fig. 3.
Mechanisms of SOCS-mediated inhibition of the JAK/STAT pathway; SOCS1 can inhibit the kinase activity of JAKs by directly binding to them, while it is thought that SOCS3 first binds to the receptor to hinder the activity of JAKs. It is believed that CIS also binds to the cytokine receptor chains, but in doing so obstructs the recruitment and therefore activation of the STAT proteins. SOCS proteins can also mediate the degradation of JAKs via the ubiquitin–proteasome system (box overlay). The highly conserved SOCS box domain directly interacts with Elongin B and C, two components of an E3 ligase complex, which then interact with Cullin-5 and RING-box 2 (Rbx2), as well as an E2 ubiquitin conjugating enzyme. The assembly of this complex allows the polyubiquitination of JAK proteins to occur, which labels them for degradation by the proteasome