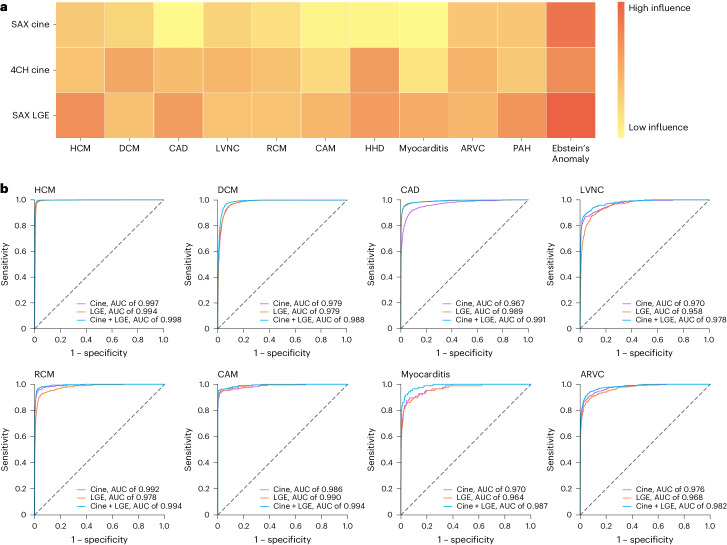
Fig. 3. Influences of individual CMR modalities.
a, Shapley values of SAX cine, 4CH cine and SAX LGE, derived from the diagnostic model (cine and LGE as combined inputs) for the prediction of each CVD class. Shapley values are displayed on a color gradient scale, with red indicating the CMR modality with the greatest influence for each CVD classification. The CMR modalities, exhibiting characteristic features for the diagnosis of the CVD class, demonstrate a consistently strong impact on their model prediction: SAX LGE for the diagnosis of CAD (distinct feature: the endomyocardial or transmural LGE matching the area of coronary artery dominance); SAX LGE for HCM (hypertrophy and RV insertion point LGE); SAX LGE for myocarditis (epicardial LGE); 4CH cine for LVNC (LV noncompaction in the apex) and 4CH cine for RCM (bi-atrial enlargement on the 4CH view). b, ROCs from the diagnostic models based on cine (purple), LGE (yellow) and cine + LGE as combined inputs (blue). Combining cine and LGE yielded the optimal diagnostic performances for all CVD classes. The performance was based on the internal test set.