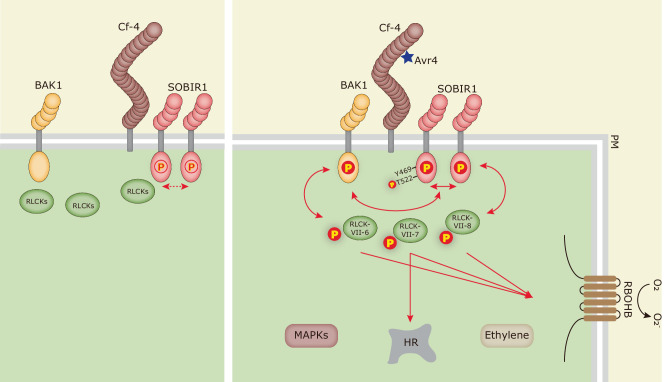
Fig. 6. Working model for the activation of the Cf-4/SOBIR1/BAK1 immune complex, and the initiation of downstream immune signalling by the activated complex.
In the absence of the Avr4 effector (left panel), the resistance protein Cf-4 constitutively interacts with SOBIR1. On the other hand, SOBIR1 constitutively forms homodimers that allow basal activation of the SOBIR1 kinase domain through cross-phosphorylation. In response to the perception of Avr4 by Cf-4 (right panel), SOBIR1 initiates strong auto-phosphorylation of its kinase domain, and the amino acid residue Thr522 is required for its intrinsic kinase activity. Meanwhile, the Cf-4/SOBIR1 complex recruits BAK1, after which trans-phosphorylation events between the cytoplasmic kinase domains of SOBIR1 and BAK1 take place. Members of the N. benthamiana RLCK-VII-6, 7, and 8 are required for the Avr4/Cf-4-triggered ROS burst, whereas members of RLCK-VII-7 are also required for the Avr4/Cf-4-induced HR. SOBIR1 Tyr469 plays an essential role in the Avr4/Cf-4-triggered HR and MAPK activation, but not in ROS accumulation and SOBIR1 intrinsic kinase activity. As this particular residue is predicted to be solvent-exposed, it is proposed that this residue regulates plant immune responses by interacting with specific downstream signalling partners. All selected RLCK-VII members can be directly trans-phosphorylated by both SOBIR1 and BAK1. Likely, these trans-phosphorylation events lead to the activation of these RLCKs, after which they can phosphorylate the RBOHB oxidase, leading to the accumulation of apoplastic ROS. Members of RLCK-VII-7 possibly phosphorylate various transcription factors or other downstream signalling components to trigger the activation of the HR. Solid arrows indicate signalling events with supporting data presented in this study, whereas dashed arrows indicate proposed events. The red open (left panel) and filled (right panel) circles with a ‘P’ inside represent low levels and high levels of phosphorylation, respectively. PM plasma membrane.