Figure 2.
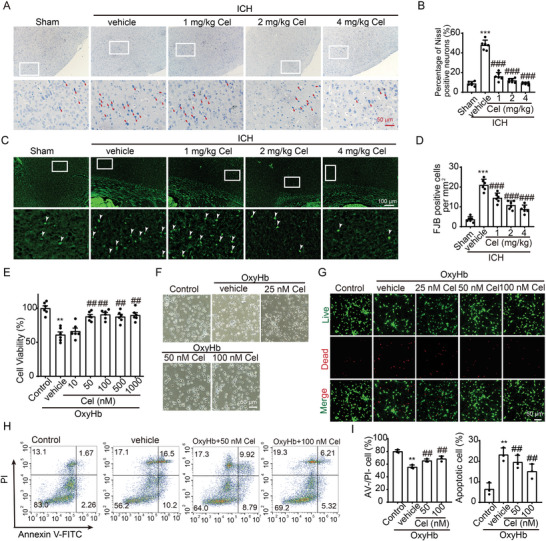
Celastrol attenuated ICH‐induced neuronal cell death. A) Nissl staining was used to assess neuronal morphology in the cortex, with arrows indicating aberrant Nissl bodies. B) The statistical analysis of abnormal Nissl bodies in the cortical region was conducted, n = 6. C) FJB staining is demonstrated, with arrows indicating the presence of FJB‐positive cells. D) The quantification of FJB‐positive cells in the perihematoma regions is presented, n = 6. The primary neurons were cultured and exposed to 10 µm oxyhemoglobin (OxyHb) for 12 h, followed by treatment with varying doses of celastrol for an additional 24 h. Subsequently, cells were harvested for the assessment of cell death indicators. E) Cell viability was assessed using the MTT assay, n = 6. F) The neuronal morphology was visualized under a microscope. G) Live‐dead cell staining was conducted to assess neuronal cell death. H) Annexin V and PI double staining combined with flow cytometry revealed neuronal apoptosis in various experimental groups in vitro. The presence of Annexin V without PI (PI−/Annexin V+) or the co‐presence of both Annexin V and PI (PI+/Annexin V+) indicated the occurrence of apoptotic neurons. I) The quantification of apoptotic cells was performed, n = 3. All data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using one‐way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons tests (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.001, *** p < 0.0001 vs sham/control group; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.001, ### p < 0.0001 vs vehicle group).
