Figure 3.
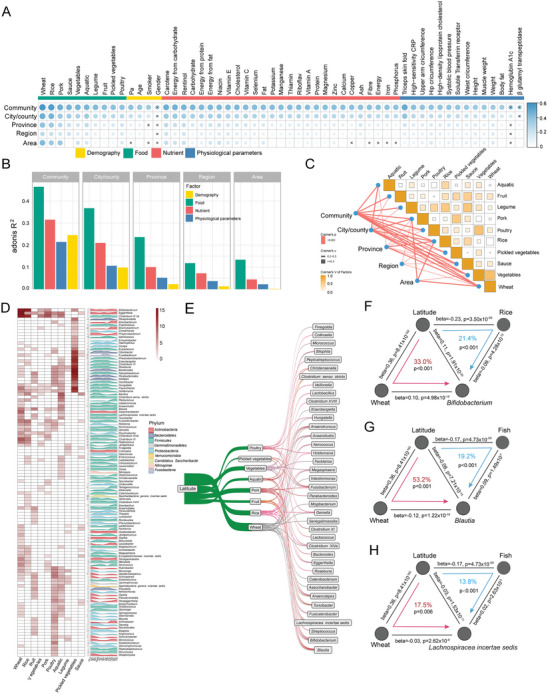
Mediation linkages among geographic location, diet, and the gut microbiome. A,B) Correlations between foods, nutrient, demographic, physiological parameters, and different geographic ranges using Cramer's V (A) and Adonis (B) (p < 0.05 and Cramer's V > 0.2). C) Correlation among 10 geography‐associated food analyzed by Cramer's V based on all samples (n = 3,181). D) The relationship between geography‐associated food and gut microbiota identified by Boruta (on the left) and the relative abundances of food‐associated microbiota in 15 provinces. The peak plots are colored according to phylum. E) Causal linkages among latitude, food, and the gut microbiota by mediation analysis (p < 0.05). F,H) Examples of causal relationships between latitude, food, and the gut microbiota. The gray lines indicate the associations. The red and blue arrowed lines indicate the latitude effects on microbiota mediated by specific food. The beta coefficient and p values are labeled at each edge. The proportions of indirect effect (mediation effect) and mediation p values are labeled at the center of the ring charts.
