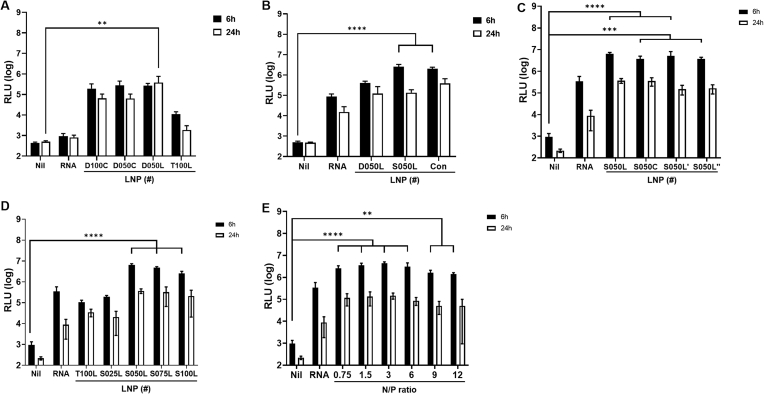
Fig. 2.
In vivo optimization of trehalose glycolipids-containing LNPs. The optimal LNPs exhibiting superior efficiency was subsequently cherry-picked, considering the interplay between helper lipids and the molar ratio of ionizable lipids. The luminescence signal of R/L at 6 and 24 h after injection of R/L mRNA⊂LNPs was expressed on a logarithmic scale. (A) A proof of concept was conducted with a primary optimizing group (LNP D100C, D050C, D050L, and T100L). (B) A cone-shaped SM-102 (LNP S050L) was replaced DLin-MC3-DMA (LNP D050L). (C) Steroid lipid structure was optimized by changing alkyl groups in steroids (LNP S050L, S050C, S050L′, and S050L″). (D) Optimization of the substitution ratio of TDO to ionizable lipid (SM-102) was investigated by changing the ratio (LNP T100L, S025L, S050L, S075L, and S100L). (E) Optimization of N/P ratio of LNP S050L. N/P ratio: moles of cationizable nitrogen in ionizable lipids divided by moles of phosphodiesters in mRNAs. Nil: the group injected with saline. RNA: the group injected with only mRNA. Data are represented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical significance was analyzed using two-way ANOVA. Statistically significant differences were defined as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001.