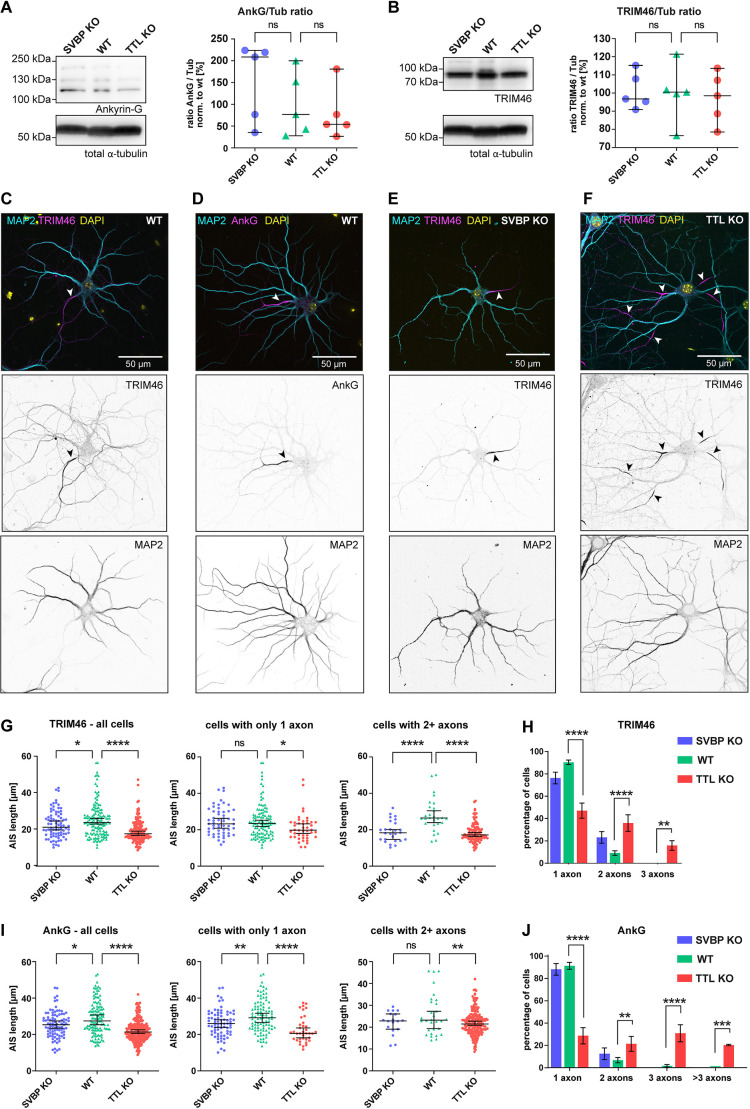
Fig. 2.
Both SVBP-KO and TTL-KO lead to shorter AIS in hippocampal neurons. (A) Western blot analysis of AnkG levels in SVBP-KO, TTL-KO and WT DIV11 primary cortical neurons. Left, representative western blot against AnkG and total α-tubulin (Tub) as loading control. Right, quantification for the ratios of AnkG to tubulin (AnkG/Tub) normalized to the mean of WT. (B) Western blot analysis of TRIM46 levels in SVBP-KO, TTL-KO and WT DIV11 primary cortical neurons. Left, representative western blot against TRIM46 and total α-tubulin as loading control. Right, quantification for ratios of TRIM46 to tubulin (TRIM46/Tub) normalized to the mean of WT. For A and B, individual values and median with 95% c.i. are shown, n=5 independent cultures, ns, not significant (Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparisons test). (C,D) Example images of WT DIV12 mouse hippocampal neurons stained for the AIS markers TRIM46 (B) or AnkG (C) together with MAP2 (dendritic marker), and DNA (DAPI). Arrowheads indicate the AIS. (E,F) Representative images of DIV12 TTL-KO (D) and SVBP-KO (E) neurons stained for MAP2, TRIM46 and DAPI. Arrowheads indicate the AIS. (G,I) AIS length of TRIM46-stained (G) and AnkG-stained (I) neurons from SVBP-KO, WT, and TTL-KO mice. Individual values and median with 95% c.i. are shown. Left panel, graphs show all cells analyzed together. Middle and right panels, graphs show cells with only 1 axon and cells with 2+ axons analyzed separately. (H,J) Quantification of neurons with supernumerary axons in the different genotypes as judged by TRIM46 (H) and AnkG (J) staining. Error bars indicate mean±s.e.m. In G–J, TRIM46, n=68, 93 and 123 AIS for SVBP-KO (two independent cultures), TTL-KO (five independent cultures) and WT (six independent cultures); AnkG, n=84, 110 and 108 AIS for SVBP-KO (three independent cultures), TTL-KO (four independent cultures) and WT (five independent cultures). ns, not significant; *P<0.05; **P<0.005; ***P<0.0005; ****P<0.0001 [Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparisons test (G,I); two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparisons test (H,J)].