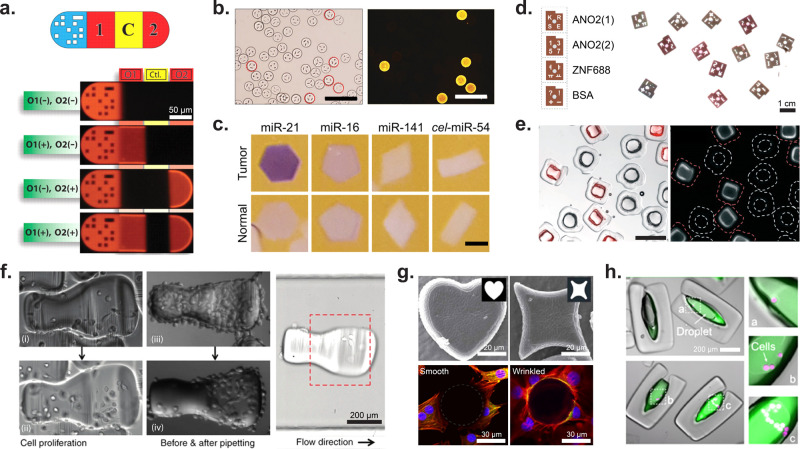
Figure 9.
Application of shaped microparticles for multiplexed and cellular assays. (a) DNA detection on barcoded particles. The particle is subdivided as follows: graphical barcode portion, detection section for DNA oligomer 1, control (should always be dark), detection for DNA oligomer 2. Particles are approximately 90 μm in width and 180–270 μm in length. [From Pregibon, D. C., et al. Multifunctional Encoded Particles for High-Throughput Biomolecule Analysis. Science2007, 315 (5817), 1393–1396 (ref (30)) reprinted with permission from AAAS.] (b) HPV DNA mutant detection where each differently shaped particle is conjugated to probes for a unique HPV DNA mutant. Images of positive particles corresponding to the barcode for HPV mutant 33. Scale bars are 200 μm. [Reproduced from Kim, L. N., et al. Chem. Commun.2015, 51 (60), 12130–12133 (ref (133)) with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry.] (c) Images showing miRNA detection (purple) from normal and tumor cells. The oncogenic miRNA, miR-21, is seen in higher concentrations in the particles incubated with tumor lysate. Slightly elevated levels of miR-16, an endogenous standard in miRNA analysis of colon cancer, was seen in the particles incubated with tumor lysate. miR-141 is a marker of poor prognosis associated with advanced colon cancer. The probe cel-miR-54 was used as a negative control. Scale bars are 200 μm. [Reproduced from Derveaux, S., et al. Anal. Bioanal Chem.2008, 391 (7), 2453–2467 (ref (135)) with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry.] (d) ELISA read out on optical scanner for the detection of autoantibodies from multiple sclerosis patients. ANO2 (1) serves as a positive control for MS autoantibodies, ANO2 (2) serves as negative control, and ZFN688 is a secondary negative control. Particles have a diameter of 900 μm and a thickness of 150 μm. [Reproduced from Svedberg, G., et al. Lab Chip2017, 17 (3), 549–556 (ref (134)) with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry.] (e) Enzyme-linked assay in particle-templated drops where the fluorescent product within a droplet supported by square particles accumulates while no fluorescent product accumulated in negative control circular particles. Particles range in size from 340–400 μm with cavity dimensions of 100–200 μm. Scale bar is 500 μm. [Reproduced from Destgeer, G., et al. Lab Chip2020, 20 (19), 3503–3514 (ref (22)) with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry.] (f) MDA-MB-231GFP cells on collagen patterned microcarriers. The first column shows cell proliferation on a microcarrier over time; the second column shows how cells on the nonshelter region were removed via pipetting while cells in the shelter area were protected from pipetting shear forces. The third image shows how the microcarrier orients in flow. Scale bar is 200 μm. [Reprinted with permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd.: Nature, Wu, C., et al. Microsyst. Nanoeng.2018, 4 (1), 21 (ref (157)) Copyright 2018.] (g) Wrinkled, nonspherical particles. The top row shows two different wrinkled particle shapes, while the bottom row shows cell adhesion differences between a spherical nonwrinkled particle (left) and a wrinkled particle (right). Scale bar is 20 μm (top) and 30 μm (bottom). [Reprinted with permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd.: Nature, Li, M., et al. Sci. Rep.2016, 6 (1) 30463 (ref (159)) Copyright 2016.] (h) LNCaP cells (magenta) encapsulated in amphiphilic particles. The fluorescence intensity of MMP-cleavable fluorogenic substrate (green) increases with increasing number of encapsulated cells. Scale bar is 200 μm. [From Wu, C., et al. Monodisperse Drops Templated by 3D-Structured Microparticles. Science Advances2020, 6 (45), eabb9023 (ref (12)) reprinted with permission from AAAS.]